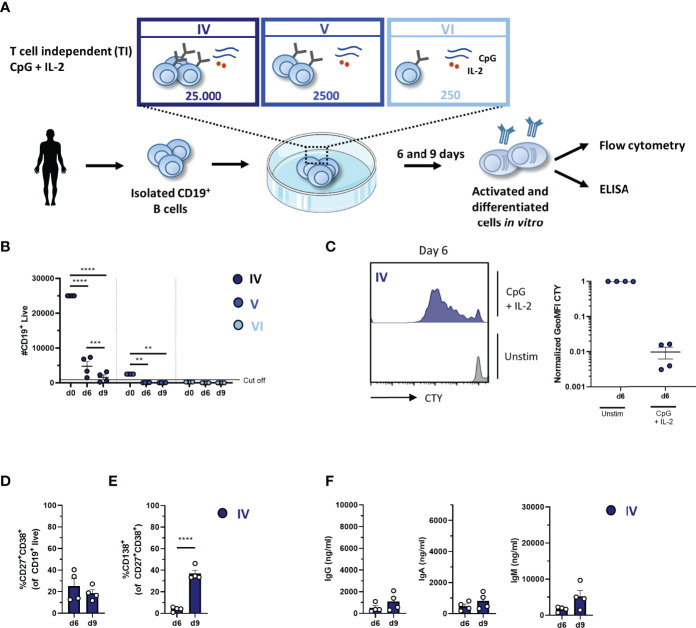
Figure 3.
Proliferation, differentiation, and antibody production after T-cell-independent in-vitro stimulation and culturing of low numbers of primary human CD19+ B cells. (A) Schematic overview of the T-cell-independent (TI) culture system to induce B-cell differentiation. A total of 25,000, 2,500, or 250 CD19+ human B cells (n = 4) were stimulated with CpG (1 µM) and IL-2 (50 ng/ml) enabling conditions IV (dark blue), V (cobalt blue), and VI (light blue). Cells were analyzed on day 6 and day 9 by flow cytometry to evaluate the (B) number of live CD19+ events, (C) amount of proliferation by CTY dilution, and frequency of (D) plasmablast (CD27+CD38+) and (E) plasma cell (CD27+CD38+CD138+) generation. A cutoff of 1,000 events was used to proceed with further analysis. (F) The supernatant was collected on day 6 and day 9 to evaluate IgG, IgA, and IgM production by ELISA (n = 4). Each data point represents the mean of an individual donor with duplicate culture measurements. Mean values are represented by bars and the error bars depict SEM. P-values were calculated using two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test (B) or unpaired t-test (D–F). **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001.