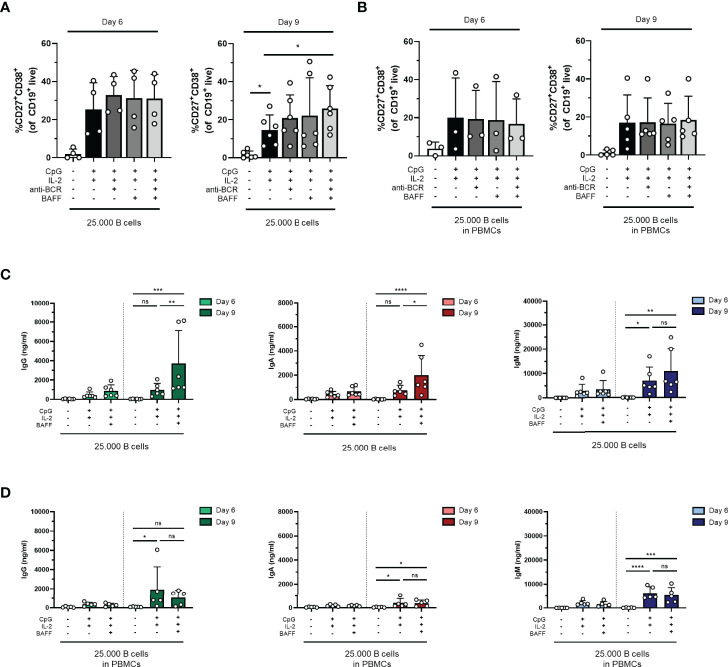
Figure 4.
The addition of BAFF in a T-cell-independent stimulation results in increased IgG and IgA production in isolated B-cell cultures. Human primary B cells obtained from healthy donors were stimulated under conditions described in Figure 3A (condition IV) and Supplementary Figure 4A (condition IV.2, PBMC cultures) with or without anti-BCR [anti-Ig F(ab)2 mix (5 µg/ml) targeting IgM, IgG, and IgA] and/or BAFF (100 ng/ml). Frequencies of CD27+CD38+ B cells on day 6 and day 9 in (A) condition IV and (B) condition IV.2 (n = 3–5). (C, D) Total secretion of IgG, IgA, and IgM measured in culture supernatants of eligible conditions after 6 and 9 days (C) without PBMCs (condition IV) and (D) as PBMC culture (condition IV.2). Each data point represents the mean of an individual donor with duplicate culture measurements. Mean values are represented by bars and the error bars depict SEM. P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (A, B) or two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test (C, D). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001. ns, not significant.