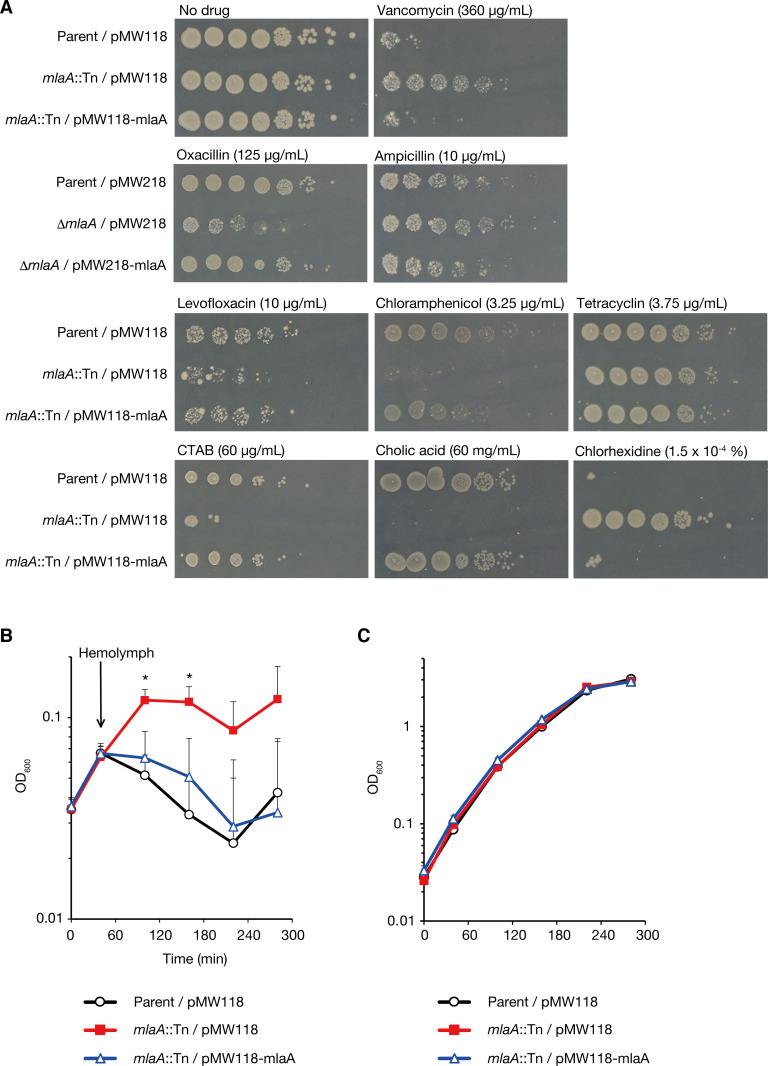
Fig 2. The mlaA-knockout mutant exhibits various sensitivities to antibiotics and resistance to silkworm antimicrobial substances.
(A) E. coli overnight culture of the Parent/pMW118, mlaA::Tn/pMW118, or mlaA::Tn/pMW118-mlaA strain was 10-fold serially diluted; spotted onto LB agar plates supplemented with or without vancomycin, levofloxacin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, CTAB, cholic acid, or chlorhexidine; and incubated at 37˚C. To examine the sensitivity to oxacillin and ampicillin, the mlaA deletion mutant (markerless deletion mutant of mlaA) transformed with pMW218 (ΔmlaA/pMW218) and the mlaA deletion mutant transformed with pMW218-mlaA (ΔmlaA/pMW218-mlaA) were used. (B) E. coli strains of the Parent/pMW118, mlaA::Tn/pMW118, or mlaA::Tn/pMW118-mlaA were aerobically cultured in LB medium and silkworm hemolymph was added to the bacterial culture at 40 min after the bacterial inoculation. The vertical axis represents the OD600 value of the bacterial culture, and the horizontal axis represents the culture time. The means ± standard errors from 5 independent experiments are shown. Star indicates Student t-test p value less than 0.05 between the Parent/pMW118 vs. mlaA::Tn/pMW118, and between mlaA::Tn/pMW118 vs. mlaA::Tn/pMW118-mlaA. (C) E. coli strains of the Parent/pMW118, mlaA::Tn/pMW118, or mlaA::Tn/pMW118-mlaA were aerobically cultured in LB medium and the OD600 values of the cultures were measured.