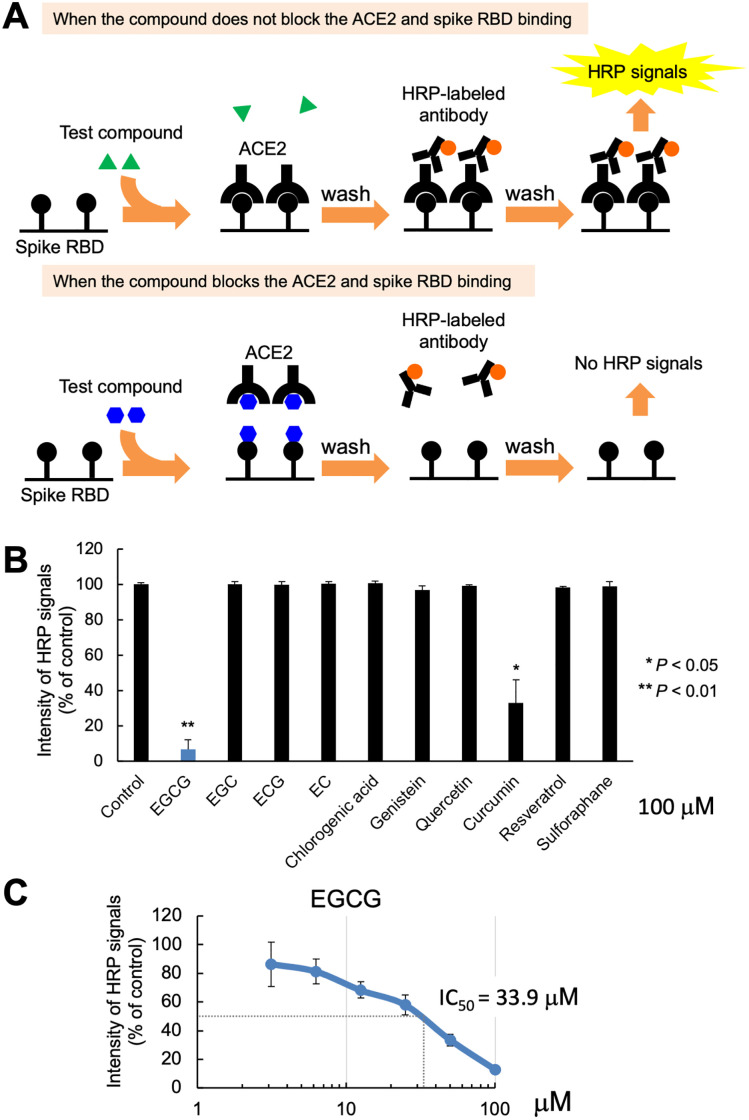
Fig 2. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) inhibits the interaction between the spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) and human cell receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).
(A) Schematic of the ELISA-based screening of phytochemical inhibitory activity on ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD binding. Upper scheme: When the compound does not block the ACE2 and spike RBD binding. Lower scheme: When the compound blocks the ACE2 and spike RBD binding. (B) ELISA results of phytochemical inhibition of the ACE2 and spike RBD binding. Low-intensity HRP signals indicate that the compound successfully blocked the ACE2 and spike RBD binding. Values are presented as the mean ± SD. Asterisks indicate the significant difference compared with the DMSO-treated control (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.05). (C) ELISA results of serially diluted EGCG (3.125–100 μM) inhibition of ACE2 and spike RBD binding b. IC50 was calculated using the IC50 calculator (https://www.aatbio.com/tools/ic50-calculator).