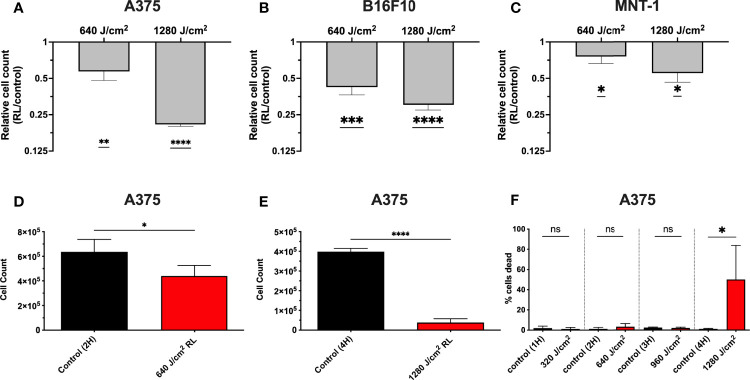
Figure 1.
RL causes a dose-dependent decrease in melanoma cell counts. (A) 48 hours after RL irradiation, relative cell counts were assessed in A375 (n=4), (B) B16F10 (n=5), and (C) MNT-1 (n=4) cells using crystal violet. The crystal violet was eluted and quantified using a Biotek plate reader, with an OD reading of 590-nm. The RL group’s 590-nm OD was indexed to matched-control for graphing of relative cell count. (D) Cell count was measured using a hemocytometer in A375 48 hours after treatment with 640 (n=4) and (E) 1280 J/cm2 (n=4). (F) Cell viability was measured using a hemocytometer 48 hours after treatment with 640 (n=4) and 1280 J/cm2 (n=4). A two-tailed T-Test (p<0.05) compared OD, cell count, and cell viability of RL treated cells to time-matched control. OD, optical density; RL, red light; 2H, 2 hours; 4H, 4 hours.*denotes p<0.05, ** denotes p<0.01, *** denotes p<0.01, **** denotes p<0.0001, and ns denotes not significant.