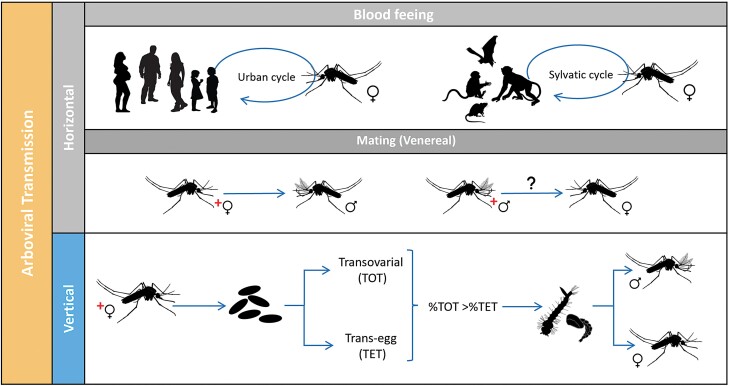
Fig. 1.
Potential transmission routes for Aedes-borne viruses: Horizontal (HT) when a female mosquito vector acquires the virus through blood-feeding on an infected vertebrate host (vector-borne transmission) is the most common and efficient route. Another type of HT includes the passage of the virus during mating (venereal transmission, HVT). Vertical transmission (TV), also called hereditary, occurs when an infected female mosquito transmits the virus to its progeny. VT can occur when germinal tissues of the female mosquitoes are infected (transovarial transmission, TOT) or during oviposition (trans-egg transmission, TET).