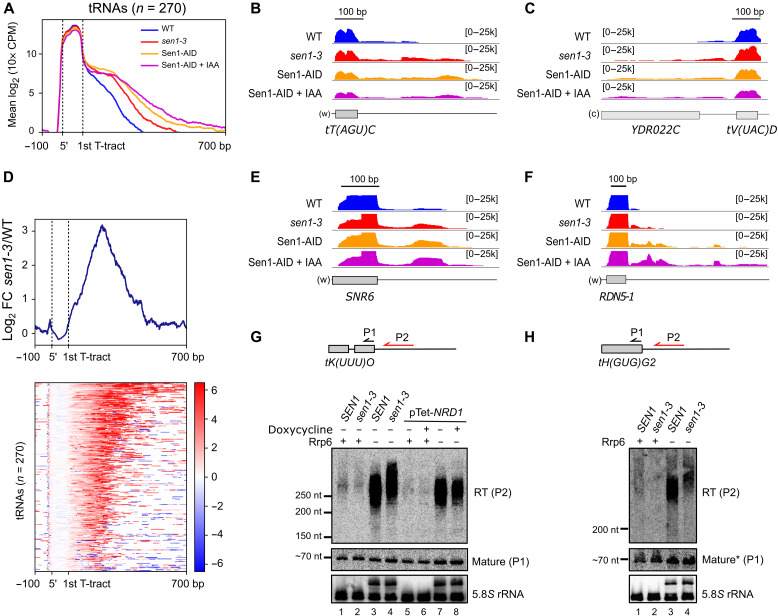
Fig. 2. The interaction of Sen1 with RNAPIII is globally required for efficient transcription termination at RNAPIII-dependent genes.
(A) Metagene analysis of the RNAPIII distribution around tRNA genes. The signal covering the region between the 5′ and the primary terminator is scaled to 100 bp. Sen1-AID, strain expressing an AID version of Sen1. (B, C, E, and F) Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) screenshots of individual genes displaying termination defects upon mutation or depletion of Sen1. “w” and “c,” Watson and Crick strands, respectively. Values under brackets correspond to the signal scale expressed in 10× counts per million (CPM). (D) Heatmap analysis representing the log2 of the fold change (FC) of the RNAPIII signal around tRNA genes in sen1-3 relative to the WT. Top: Summary plot of the mean values. (G and H) Northern blot analysis of transcripts derived from two tRNA genes in the indicated backgrounds. The approximate position of the probes (P1 and P2) used for the detection of the different RNA species (RT and mature tRNA) is shown on the top. RNA and DNA probes are indicated in red and black, respectively. pTet-NRD1, strain/s expressing NRD1 from a Tet-Off promoter. Nrd1 was depleted by incubation with doxycycline for 10.5 hours. The 5.8S rRNA is used as a loading control. 5.8S precursors are detected in the Δrrp6 background because Rrp6 processes the 5.8S. An asterisk indicates that the signal of mature tH(GUG)G2 corresponds to the same samples loaded in the blot in (G).