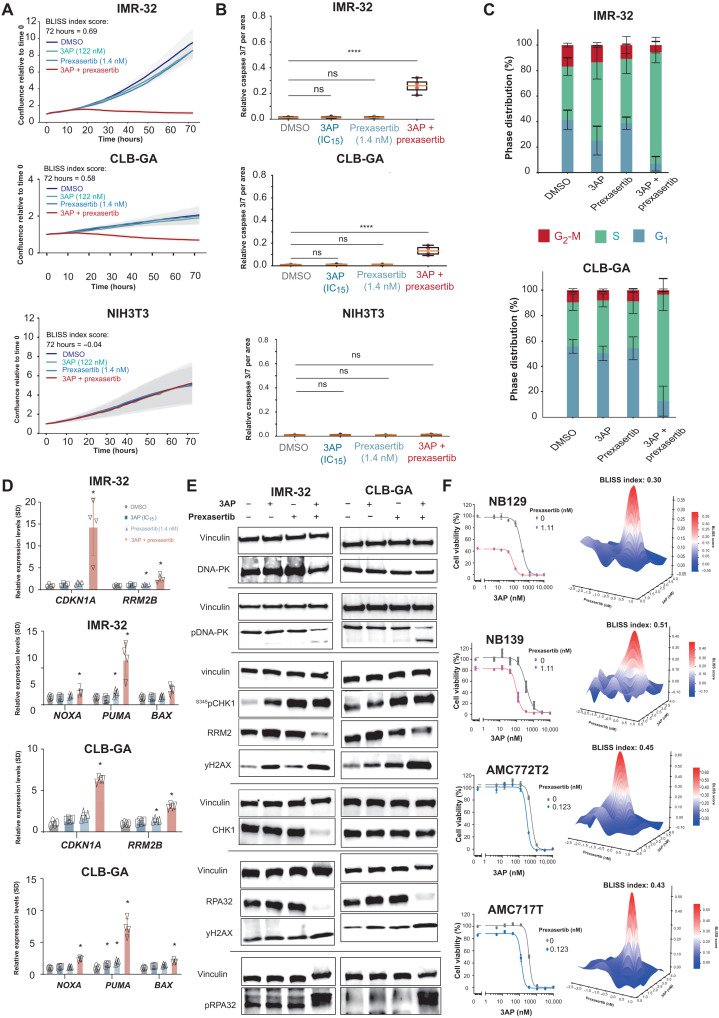
Fig. 7. Identification of 3AP-prexasertib as a synergistic drug combination in neuroblastoma.
(A) IncuCyte live cell imaging indicates a drug synergism between RRM2 and CHK1 pharmacological inhibition resulting in reduced cell confluence in IMR-32 and CLB-GA neuroblastoma cells, while not affecting NIH3T3 confluence. (B) Combined 3AP-prexasertib treatment of IMR-32 and CLB-GA neuroblastoma cells leads to a significant induction of apoptosis compared to a single compound treatment or DMSO-treated cells, while NIH3T3 cells did not show any apoptotic response. (C) Combined 3AP-prexasertib treatment of IMR-32 and CLB-GA neuroblastoma cells results in a strong S phase arrest compared to a single compound treatment or DMSO-treated cells. (D) RT-qPCR analysis for the p53 targets CDKN1A and RRM2B as well as the proapoptotic genes BAX, NOXA, and PUMA upon combined 3AP-prexasertib treatment. (E) Immunoblotting for various DNA damage markers in IMR-32 and CLB-GA cells upon treatment with DMSO or 3AP or prexasertib as a single agent or combined 3AP and prexasertib (see quantification in fig. S2). (F) 3AP-prexasertib combined treatment synergistically affected neuroblastoma spheroid cell viability 120 hours after treatment.