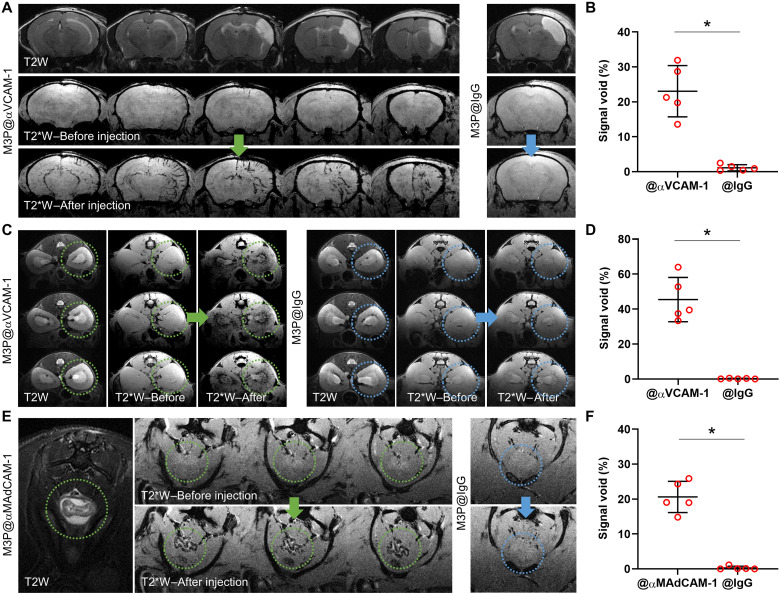
Fig. 6. Molecular imaging of endothelial activation in clinically relevant experimental models.
(A) Representative T2-weighted and T2*-weighted images before and after intravenous injection of M3P@αVCAM-1 (left) or M3P@IgG (right) (4 mg/kg) 24 hours after ischemic stroke induction by electrocoagulation of the right middle cerebral artery. (B) Corresponding quantification of signal void in the right hemisphere (n = 5 per group). (C) Representative T2-weighted and T2*-weighted images before and after intravenous injection of M3P@αVCAM-1 (left) or M3P@IgG (right) (4 mg/kg) 48 hours after acute kidney injury (rhabdomyolysis) induced by intramuscular injection of 50% glycerol. Yellow and blue dotted circles indicate the localization of the right kidney. (D) Corresponding quantification of signal void in the kidney medulla (n = 5 per group). (E) Representative T2-weighted and T2*-weighted images before and after intravenous injection of M3P@αMAdCAM-1 (left) or M3P@IgG (right) (4 mg/kg) in an acute colitis model induced by 5-day treatment with 2.0% of dextran sodium sulfate in the drinking water. Yellow and blue dotted circles indicate the localization of the descending colon. (F) Corresponding quantification of signal void in the descending colon (n = 5 per group). *P < 0.05.