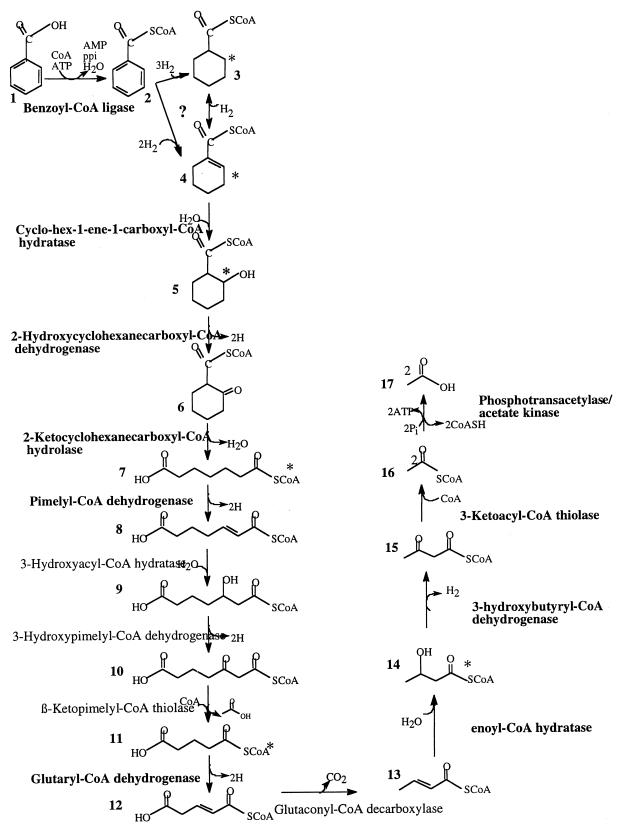
FIG. 4.
Proposed pathway for benzoate metabolism in “S. aciditrophicus.” Enzyme activities detected in “S. aciditrophicus” cell extracts are indicated by boldface type. The asterisks indicate compounds detected as their TMS derivatives in “S. aciditrophicus”-M. hungatei coculture extracts. 1, Benzoate; 2, benzoyl-CoA; 3, cyclohexane carboxyl-CoA; 4, cyclohex-1-ene carboxyl-CoA; 5, 2-hydroxycyclohexane carboxyl-CoA; 6, 2-ketocyclohexane carboxyl-CoA; 7, pimelyl-CoA; 8, 2-heptenedioc acid-1-CoA; 9, 3-hydroxypimelyl-CoA; 10, 3-ketopimelyl-CoA; 11, glutaryl-CoA; 12, glutaconyl-CoA; 13, crotonyl-CoA; 14, 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA; 15, acetoacetyl-CoA; 16, acetyl-CoA; 17, acetate. The question mark indicates that the exact benzene ring reduction mechanism in “S. aciditrophicus” is not completely understood yet.