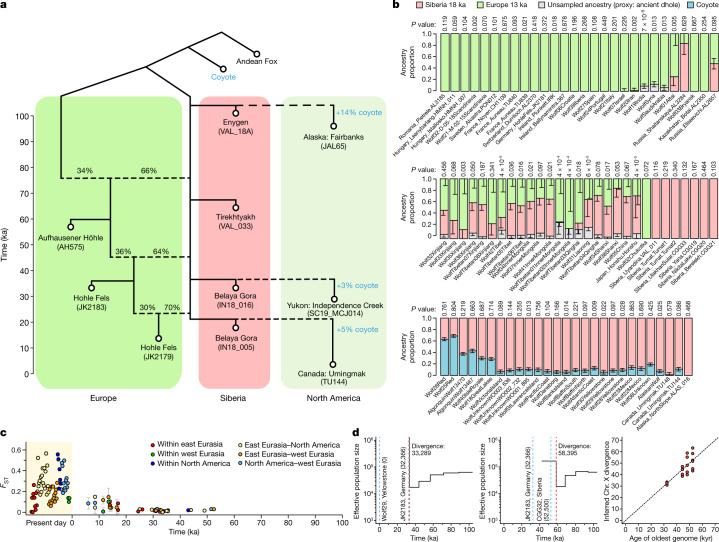
Fig. 2. One hundred thousand years of wolf population history.
a, Admixture graph fit by qpGraph to selected ancient wolves, with two outlier (|Z| > 3) f-statistics (worst = 3.16). b, Best-fitting qpAdm models for post-LGM and present-day wolves. An ancient dhole was used as the outgroup for Eurasian wolves to capture any unsampled divergent ancestry, while a coyote was used as the outgroup for North American wolves. Bars denote ±1 standard error estimated from a block jackknife. c, FST for pairs of sample groups with mean dates separated by ≤12,500 years. Bars denote ±1.96 standard errors d, MSMC2 results for pairs of male X chromosomes, with sample ages indicated by blue lines. A sharp upwards spike in the curve corresponds to population divergence, with estimated timings indicated by red lines. Example curves for two pairs of wolves (left and middle) and a summary of results for all pairs (right) are shown. kyr, thousand years.