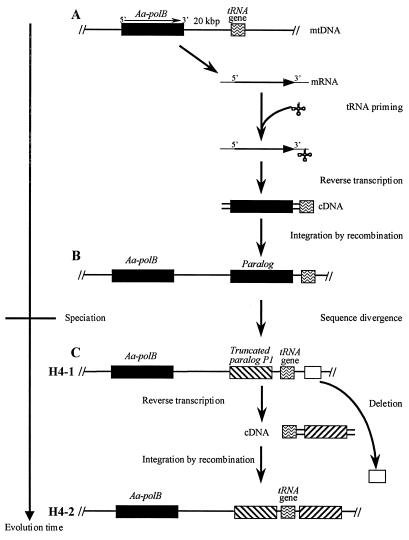
FIG. 3.
Hypothetical model for the duplications of the family B DNA polymerase genes in the A. aegerita mitochondrial genome. (A) Distal (20-kb) duplication involving reverse transcription (RT) of the Aa-polB mRNA primed by the tRNAMet followed by integration of the cDNA (Aa-polB-tRNAMet) by recombination at the tRNAMet locus. (B) Sequence divergence (up to 14%) between Aa-polB and its paralog, leading to the disruption of the Aa-polB P1 copy. (C) Proximal (317-nt) duplication generating two inverted copies of Aa-polB P1 by recombinational integration at the tRNAMet locus of a cDNA (Aa-polB P1-tRNA) obtained after RT of the Aa-polB P1 mRNA. This duplication is accompanied by a large (>0.6-kb) deletion of neighboring mitochondrial sequences.