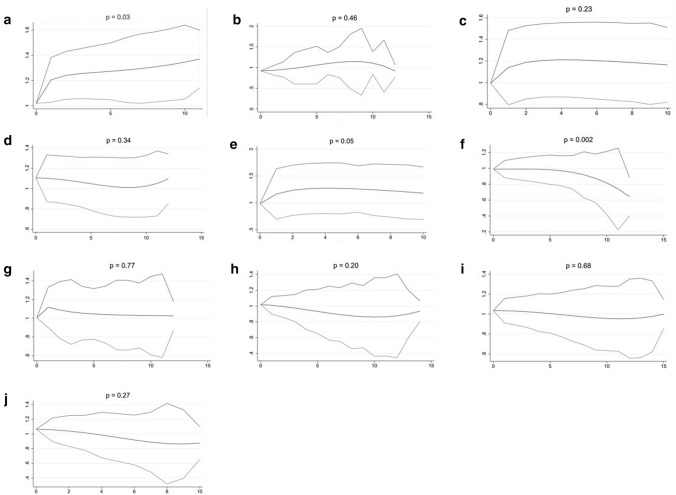
Fig. 1.
Dose–response analyses (x-axis: dose (defined per vitamin or vitamin group, see below), y-axis: HR for BC, with 95% confidence interval); a thiamin (B1) (dose = 300 µg), b riboflavin (B2) (dose = 800 µg), c niacin (B3) (dose = 2500 µg), d pyridoxine (B6) (dose = 300 µg), e folate (B9 (dose = 30 µg)), f cyanocobalamin (B12) (dose = 1.5 µg), g vitamins related to energy metabolism (dose = 1.25 × 1011 µg), h vitamins related to the reduction of oxidative stress (dose = 5.0 × 106 µg), i vitamins related to DNA stability (dose = 200 µg) and j the entire B group vitamin complex (dose = 1.0 × 1016 µg)