Figure 7.
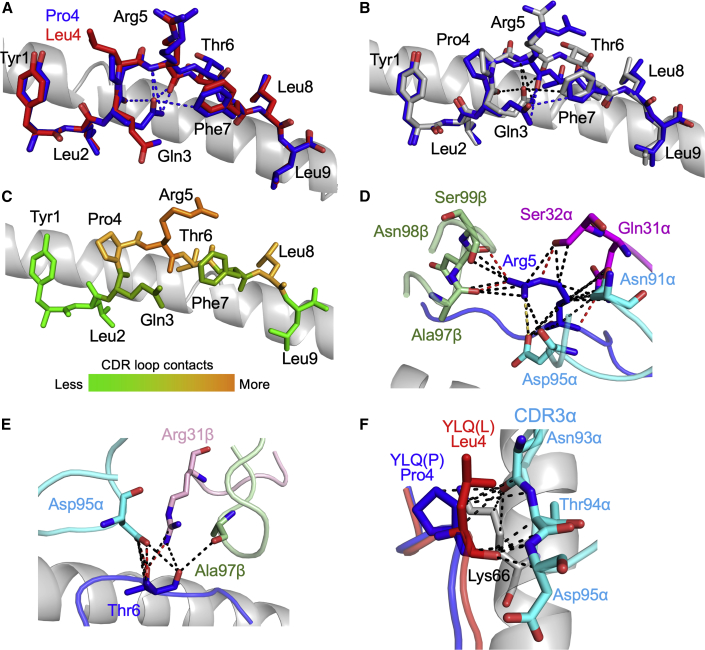
3D structure of antigens and YLQ36 TCR HLA A∗02:01-YLQPRTFLL complex
(A) Comparison of HLA A∗02:01-YLQPRTFLL (blue sticks) and HLA A∗02:01-YLQLRTFLL (red sticks). HLA A∗02:01 shown as grey cartoon. Intrapeptide bonds present in HLA A∗02:01-YLQPRTFLL are shown as blue dashes.
(B) Comparison of unbound HLA A∗02:01-YLQPRTFLL (grey sticks) and TCR-bound HLA A∗02:01-YLQPRTFLL (blue sticks) peptide presentation. HLA A∗02:01 shown as grey cartoon. Intrapeptide bonds present in unbound HLA A∗02:01-YLQPRTFLL and TCR-bound HLA A∗02:01-YLQPRTFLL are shown as black and blue dashes, respectively. See Figure S6 for the sequence of the YLQ36 TCR.
(C) Heat map of YLQ36 TCR contacts with the YLQPRTFLL peptide.
(D) YLQPRTFLL peptide residue Arg5 shown as blue sticks. Important YLQ36 TCR residues are labeled. Black dotted lines indicate van der Waals interactions. Red dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds. Yellow dotted lines indicate salt bridges.
(E) YLQPRTFLL peptide residue Thr6 shown as blue sticks. Important YLQ36 TCR residues are labeled. Black dotted lines indicate van der Waals interactions. Red dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
(F) YLQPRTFLL and YLQLRTFLL P4 residues shown as blue and red sticks, respectively. Important HLA A∗02:01 residues shown as grey sticks. YLQ36 CDR3α loop shown as cyan sticks. Interactions involving the YLQ36 CDR3α loop are shown as black dashes. Also see Figure S7.
.