FIGURE 2.
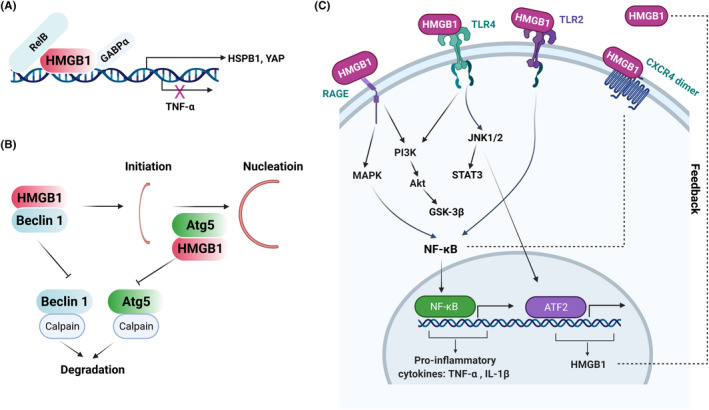
Schematic diagram of HMGB1’s function in the cytoplasm, nucleus and extracellular spaces. (A) In the nucleus, HMGB1 binds (such as promotors of YAP, HSBP1) and bends DNA, which maintains genome stability and regulates gene transcriptions. (B) In the cytoplasm, HMGB1 binds to protein partners and facilitate various cellular function, such as the binding of Beclin1 in the process of autophagy. (C) In the extracellular space, HMGB1 binds to several receptors, such as TLR2, TLR4 and RAGE, and regulates downstream signalling pathways, including MAPK, PI3K, NF‐κB and JAK/STAT, which are essential in signalling network of diseases
