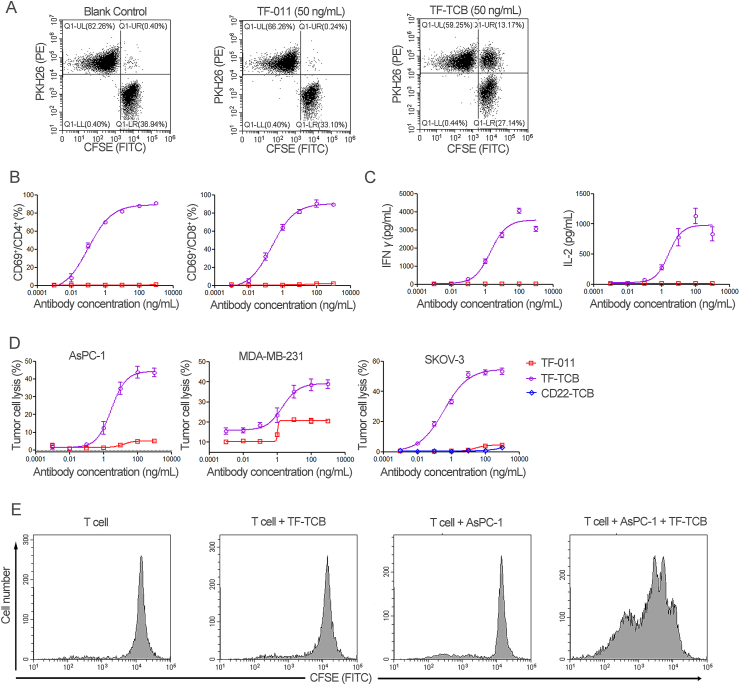
Figure 3.
Mechanism of action of TF-TCB. (A) Cross-linking of CD3+ Jurkat cells and TF+ AsPC-1 cells by TF-TCB measured through flow cytometry. Jurkat cells were labeled with PKH26 (PE) and AsPC-1 cells were labeled with CFSE (FITC), the two cells were mixed at equal ratio in the presence of TF TCB (or TF-011) and incubated for 30 min. (B) and (C) T cell activation and cytokine release mediated by TF-TCB. T cell activation (B) was assessed by measuring percentage of CD69+ cells within CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after 20 h of incubation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) with AsPC-1 cells (E:T, 10:1) and TF-TCB. IFNγ and IL-2 released into culture supernatant were also determined (C). TF-011 was used as control. (D) Percentage of tumor cell lysis detected after incubation of AsPC-1 (36 h), MDA-MB-231 (24 h) and SKOV-3 cells (36 h) with PBMC and TF-TCB. TF-011 and CD22-TCB were used as controls. (E) T cell proliferation evaluated through the decrease in CFSE labeling on T cells. Purified T cells were labeled with CFSE (FITC) and incubated with or without AsPC-1 cells, in the presence of TF-TCB or not for 96 h, and the CFSE labeling on T cells was evaluated by flow cytometry. Data are mean ± SD, n = 3.