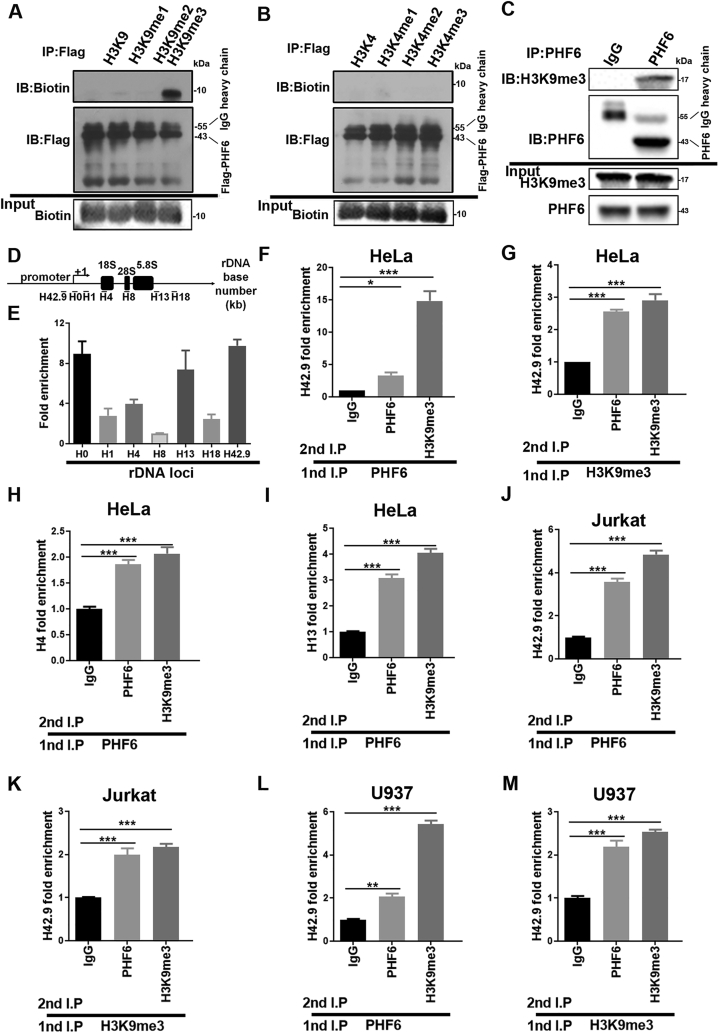
Figure 2.
PHF6 selectively recognizes and binds to the heterochromatin-associated histone marks. (A)–(B) Co-IP analysis of Flag-PHF6 binding to histone methylation mimic peptides. The upper graph shows the amount of various mimic polypeptides that interact with Flag-PHF6. The middle graph shows the amount of Flag-PHF6 in the Flag antibody conjugate. The lower graph shows the amounts of mimic polypeptides added. (C) Co-IP analysis of histone H3 containing the trimethylated lysine 9 (H3K9) with PHF6 in HeLa cells. (D) Schematic diagram of human rDNA gene repeat sequence and positions of ChIP-qPCR primers. (E) ChIP assays were performed using control IgG and PHF6 antibodies, and the precipitated DNA was then analyzed using qPCR with the aforementioned primers. The relative rDNA fold-enrichment was normalized to control IgG treatment. (F)–(M) Re-ChIP experiments detected the binding of PHF6 to H3K9me3 at the rDNA loci using H4, H13, and H42.9 primers. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. All values are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 3.