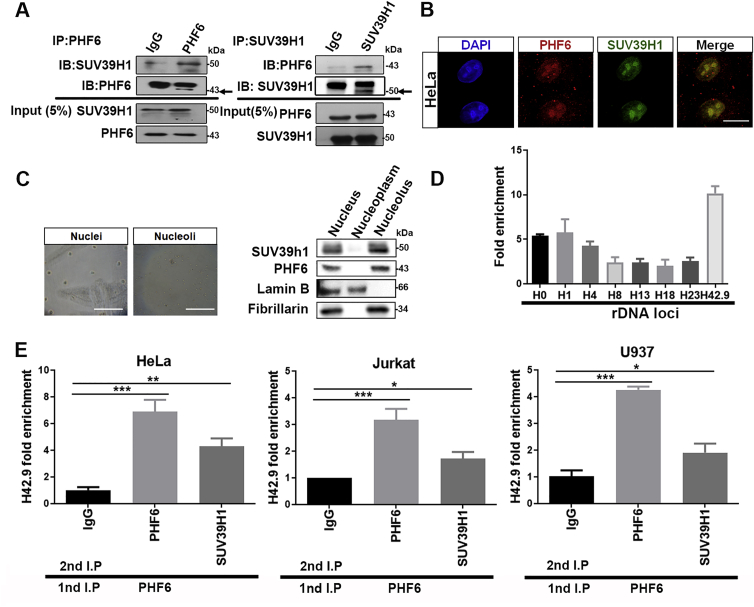
Figure 3.
PHF6 interacts with SUV39H1 in the nucleolus, and they accumulate together in the rDNA loci. (A) Co-IP analysis of SUV39H1 with PHF6 in HeLa cells. (B) Confocal images of HeLa cells to show PHF6 (red fluorescence) colocalized with SUV39H1 (green fluorescence) in the nucleoli. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) HeLa cells were fractioned into nuclear (left image), nucleoplasm and nucleolar (right image) fractions, and the proteins were detected by Western blotting using the antibodies described. Lamin B and fabrillarin are the nuclear and nucleolar markers, respectively. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) ChIP assays were performed with control IgG and SUV39H1 antibodies, and the precipitated DNA was then analyzed using qPCR with the forementioned primers. The relative rDNA fold-enrichment was normalized to control the IgG treatment. (E) Re-ChIP experiments detected the binding of PHF6 to SUV39H1 in HeLa, Jurkat and U937 cells. The primer H42.9 was used for detection using real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. All the values are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 3.