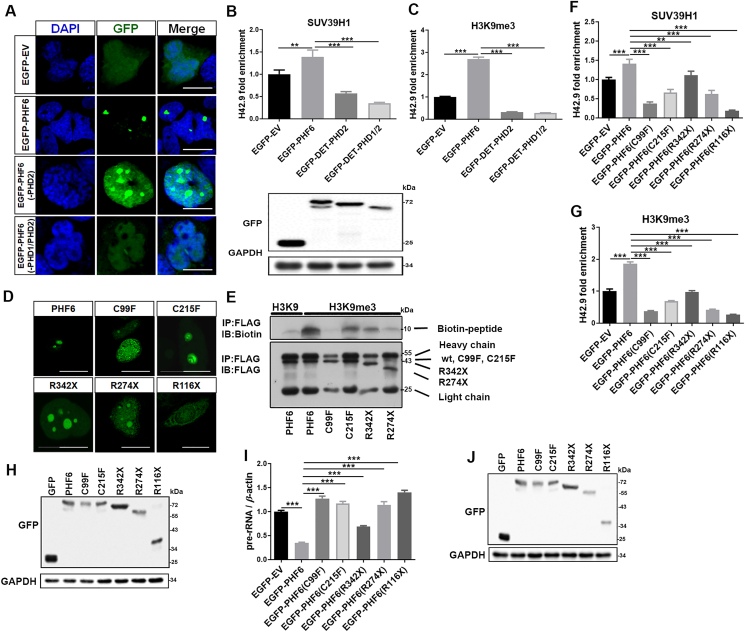
Figure 5.
PHF6 mutants are less able to bind H3K9me3 peptides and recruit SUV39H1. (A) Confocal images of HeLa cells that were transfected with EGFP-EV, EGFP-PHF6, EGFP-PHF6 (-PHD2), and EGFP-PHF6 (-PHD1/PHD2) plasmids. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) and (C) ChIP analysis of SUV39H1 (B) and H3K9me3 (C) at the rDNA loci in (A) cells. Western blot results show the protein levels of EGFP-PHF6. (D) Confocal images of HeLa cells that were transfected with the clinical PHF6 mutants indicated. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Co-IP analysis of Flag-PHF6 and its mutants binding to peptides that mimic H3K9me3. (F) and (G) ChIP analysis of SUV39H1 (F) and H3K9me3 (G) binding to rDNA loci in HeLa cells that were transfected with the plasmids indicated. (H) Immunoblot of GFP in indicated cell lysates (F and G). (I) qPCR analysis of 47S pre-rRNA from HeLa cells that were transfected with the plasmids indicated. (J) Immunoblot of GFP in HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. All values are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 3; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001.