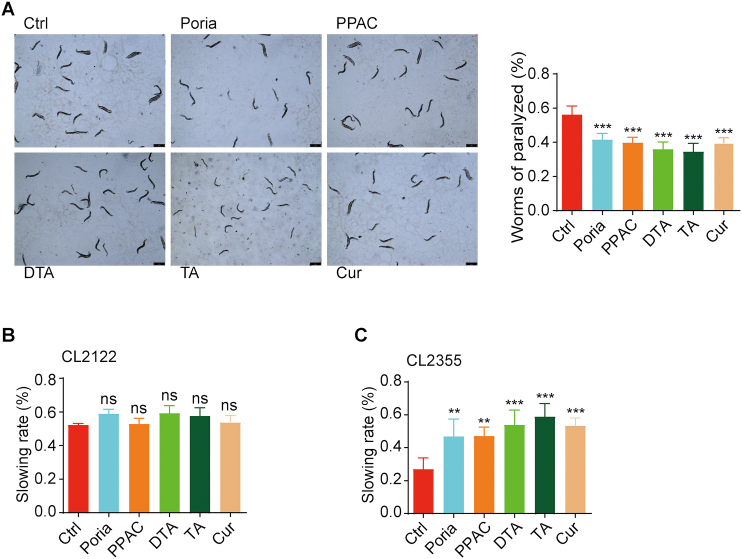
Figure 5.
PPAC, DTA, and TA improve the behavioral function in C. elegans. (A) Aβ1–42-induced CL4176 worms were treated without or with Poria extract, PPAC, DTA, TA or Cur for 72 h. After treatment, the representative images of worms were captured by a microscope at 10×magnification (Scale bars: 100 μm). The bar chart represents the quantification of worms (n > 60) that were not paralyzed. (B, C) Aβ-induced C. elegans CL2355 and its control strain CL2122 were treated with Poria extract, PPAC, DTA, TA or Cur for 72 h. After treatment, the food-sensing behavior was evaluated by counting the body bends of worms per 20 s on NGM plates in the absence or presence of food. The bar charts indicate the slowing rate of worms (n = 20). All data are representative of at least three independent experiment and are presented as mean ± SD. ns: not significant, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Poria extract: 500 μg/mL; PPAC: 100 μmol/L; DTA: 100 μmol/L; TA: 100 μmol/L; Cur: 100 μmol/L.