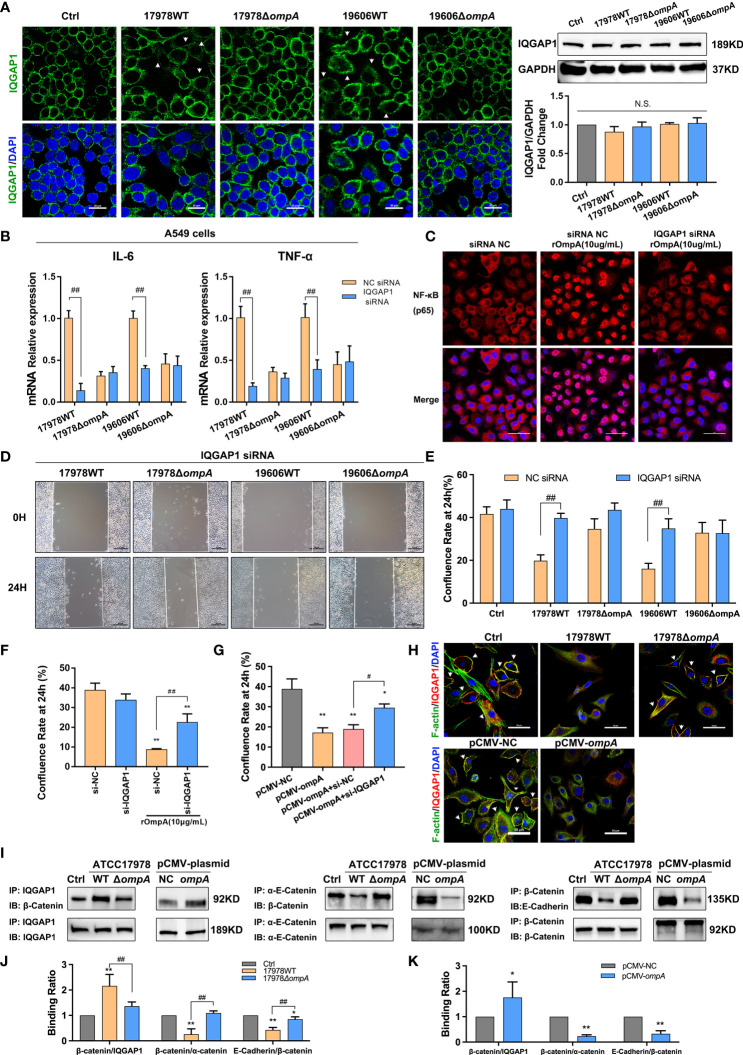
Figure 6.
OmpA-dependent inflammatory regulation and cytoskeleton/cell junction dysfunction require IQGAP1 in epithelial cells. (A) Redistribution of IQGAP1 was evaluated by immunofluorescence labeling (arrows). Green represents IQGAP1 and blue indicates nuclei. Scale bar: 20 μm. Expression of IQGAP1 was evaluated by Western blotting. The IQGAP1 protein level is shown relative to GAPDH. (B, C) The effects of IQGAP1 knockdown on IL-6 and TNF-α expression level (B) and NF-κB activation (C) in A549 cells infected with different A. baumannii strains. Red represents NF-κB and blue indicates nuclei. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D–G) The effects of IQGAP1 knockdown on migration ability of A549 cells infected with different A. baumannii strains (D, E), treated with rOmpA (F), or transfected with pCMV-ompA expression plasmid (G). (H) The co-localisation of IQGAP1 and F-actin was detected by immunofluorescence; the interaction of IQGAP1 with E-cadherin–catenin complex in A549 cells was detected by co-immunoprecipitation assay, green represents F-actin, red represents IQGAP1, yellow represents IQGAP1/F-actin co-localization (arrows) and blue indicates nuclei, scale bar, 50μm. (I–K) The binding ability of β-catenin/IQGAP1, β-catenin/α-catenin and E-Cadherin/β-catenin in A549 cells infected with different A baumannii strains or transfected with pCMV-ompA expression plasmid were expressed as the ratio of β-catenin (IP) to IQGAP1 (IP), β-catenin (IP) to α-catenin (IP) and E-Cadherin (IP) to β-catenin (IP). **P<0.01,*P<0.05 vs. Control (or NC siRNA, pCMV-NC) group, ## P<0.01, # P<0.05; N.S., no significance.