Figure 1.
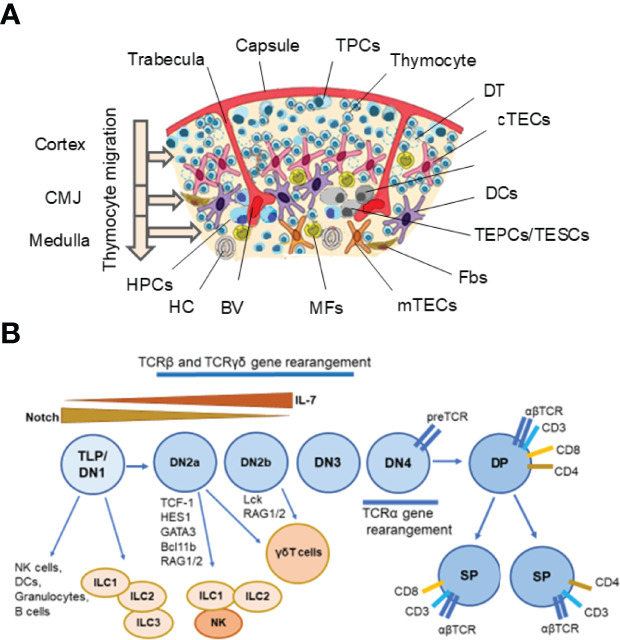
Thymus cell architecture (A), and T cell and innate lymphoid cell (ILC) development in the thymus (B). The thymus consists of two lobes that are separated by connective tissue strands (trabeculae) in lobules. Each thymic lobule consisted of the cortex and medulla. The cortex contains CD34+ uncommitted pluripotent hematopoietic precursor cells (HPCs) entering the thymus at the cortico-medullary junction (CMJ) and migrating to the capsule, committed double negative (DN) CD4−CD8− T precursor cells (TPCs) located in the subcapsular region (DN1–DN4 stages), and immature double positive (DP) CD4+CD8+ (Pre-DP) cortical thymocytes migrating through the cortex and CMJ to the medullar zone. The medulla contains single positive (SP) CD4+ and CD8+ naïve thymocytes migrating to the periphery after maturing. Stromal-epithelial compartment of the thymus is submitted by minor populations of EpCam+ (CD326+) Foxn1+ bipotent thymic epithelial precursor cells/thymic epithelial stem cells (TEPCs/TESCs), and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) located probably into the thymic parenchyma close to the CMJ region, as well as EpCam+CD205+ cortical thymic epithelial cells (cTECs) located in the cortex and EpCam+Air+ medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) located in the medulla. The cortex and medulla also contain macrophages (MFs), fibroblasts (Fbs), and dendritic cells (DCs) that, together with cTECs and mTECs, participate in the differentiation, maturation, and positive and negative selection of thymocytes. T cell and ILC lineages diverge at the stages of early T precursors/double negative 1 (ETP/DN1) and the DN2-DN3 transition stage. Depending on the status of the TCR loci, the strength of Notch signaling and activities of E-ld proteins and Bcl11b, multipotent TLPs may develop conventional αβ T cells or acquire innate-like properties and give rise to thymic natural killer (NK) cells, DCs, granulocytes, B cells, one of three ILC subsets and invariant γδ T cells. Resident ILC progenitors have been suggested to originate from failed T cell development and locally maintain the mature ILC pool. BV, Blood Vessel; DT, Dead Thymocytes; HC, Hassall’s Corpuscle. (A) modified from Shichkin and Antica, 2020 (9); the article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. (B) modified from Shin and McNagny, 2021 (138); the article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY).
