Fig. 5.
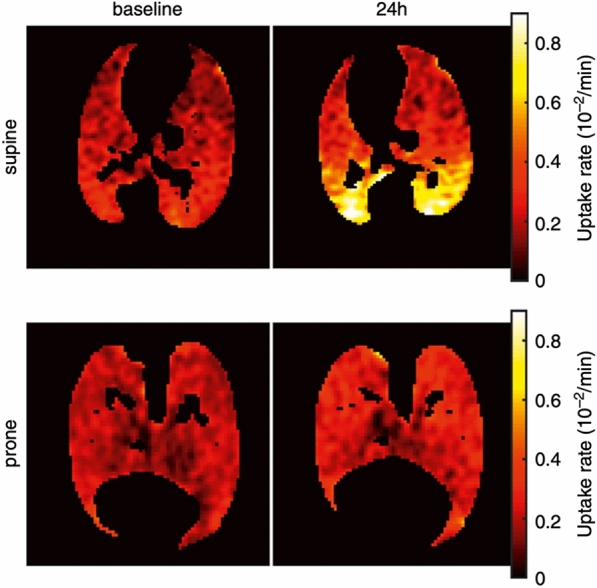
Lung cellular metabolic activity assessed in PET in animals with ARDS in the supine and prone position. The figure shows the tissue-corrected [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose cellular uptake rate, a marker of cellular metabolism and inflammation in the lungs of sheep before and after 24 h of experimental ARDS and mechanical ventilation. Animals are compared based on their body position (supine vs. prone). The figure illustrates how prone positioning (PP) may decrease the inflammatory response of dependent regions that appear in supine animals after 24 h. The article from which this figure is taken suggests that the prevention of lung inflammation is related to the decrease in regional lung strain allowed by PP in posterior regions. Adapted with permission from the American Thoracic Society. Copyright © 2022 American Thoracic Society. All rights reserved [39]
