FIGURE 2.
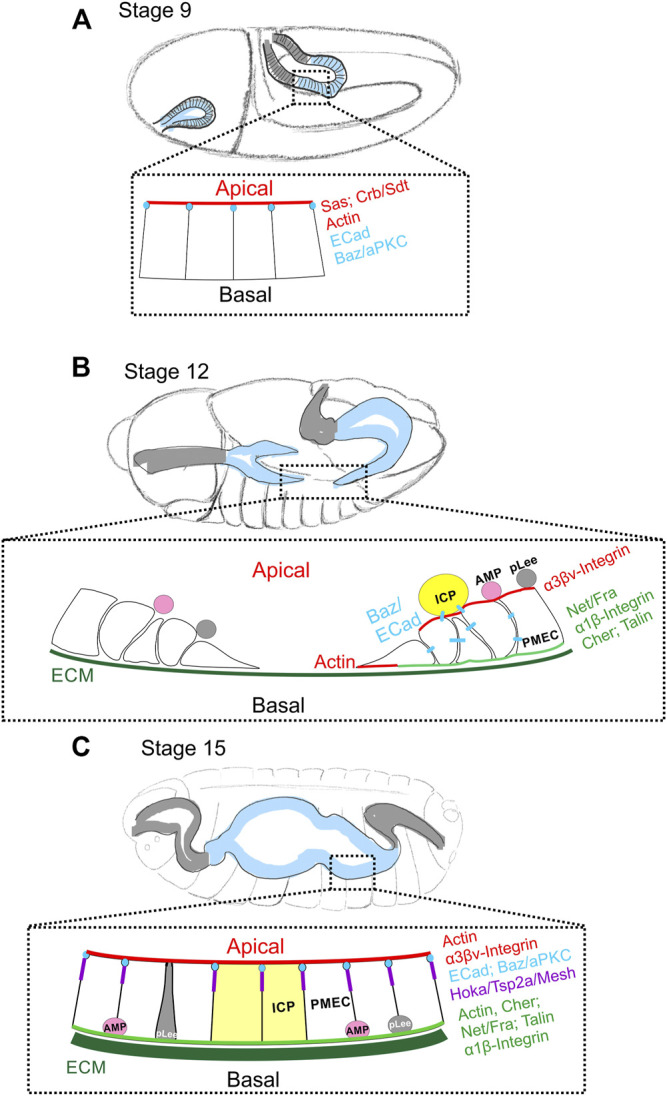
Changes in cell polarity during embryonic midgut formation. (A) During gastrulation at stage 9, the endoderm (blue shaded region) and ectoderm of the hindgut (gray shaded region) invaginate. The posterior midgut (all esg+) is still an epithelium with Sas and Crb/Sdt at the apical domain (red) and Ecad and Baz/aPKC at the apical AJs (blue). At this stage, the visceral muscle layer is not yet fully formed, and no clear basal features have been described. (B) By stage 12, Crb/Sdt and Sas have disappeared from the midgut primordia and the cells have undergone EMT and become migratory. The presumptive posterior and anterior midgut rudiments migrate along the visceral mesoderm towards each other. ECM (dark green) components can be found between the endoderm and visceral mesoderm by late stage 12. The posterior midgut primordium segregates into principal midgut epithelial cells (PMECs), Interstitial cell precursors (ICPs; yellow) and adult midgut precursors (AMPs; pink), while the anterior primordium contains only PMECs and AMPs. ICPs to delaminate first, followed by the AMPs and both remain attached to the migrating PMECs. At stage 11, the inner layer of migrating mesenchyme also contains esg + Pros + cells, possibly the progenitors of the larval ee cells (pLees; gray). Both the AMPs and pLees remain attached to PMECs until later stages. Actin is enriched at the basal, migratory front and Baz (blue) can be found at spot AJs between PMECs and ICPs. Behind the migrating front, PMEC cells start to repolarise. Talin and Filamin1/Cher are localised basally (green) together with Fra and the α1/β-integrin complex, while the α3βν-integrin complex localises apically (red). (C) By stage 15, the anterior and posterior midgut primordia have fused and the presumptive midgut has closed ventrally and dorsally to form a continuous tube. ECM (dark green) forms a more complex network at this stage. The repolarised PMECs start to form smooth SJs (purple). ECad and Baz localise to the apical junctions (blue), Actin to both the apical and basal sides and Filamin-1/Cher to the basal domain. Fra and the α1β-integrin complex remain at the basal domain (green), while the α3βν-integrin complex localises mainly apically (red). By the end of embryonic development, ICPs (yellow) have integrated into larval midgut epithelium and AMPs (pink), which are the only remaining esg + cells, have translocated to the basal side of the epithelium. It is not known when the pLee cells (grey) integrate into the epithelium.
