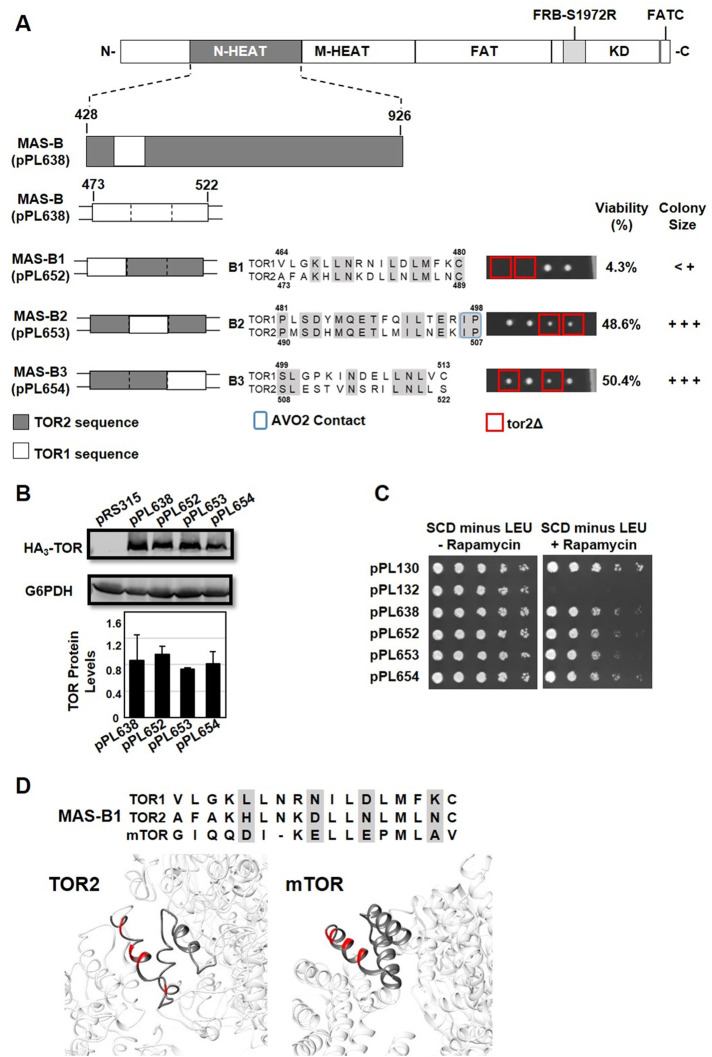
FIGURE 6:
Identification of functional elements within the TOR2 MAS-B chimera. (A) MAS-B plasmid pPL638 containing the S1972R (RapR) TOR1-1 allele was modified to create the indicated TOR1-TOR2 chimeras. Each construct, B1 through B3, contains approximately 6–10 amino acids of TOR1 sequence within an otherwise TOR2 MAS domain, as depicted in the indicated sequence alignments for TOR1 and TOR2. Predicted amino acids contacts between TOR2 and AVO2 are boxed in blue in construct TOR2 MAS B-2. Plasmids were introduced into heterozygous TOR2/tor2Δ cells and analyzed by tetrad dissection as described in the legend to Figure 3A. (B) Western blot analysis of TOR1-TOR2 chimeras. TOR2/tor2Δ cells carrying the indicated plasmids were prepared and analyzed as described in the legend to Figure 2D. (C) TOR2/tor2Δ cells carrying the indicated plasmids were tested for rapamycin resistance as described in the legend to Figure 3B. (D) Sequence alignment of MAS-B1 in TOR1, TOR2, and mTOR, highlighting four nonconservative amino acid changes between TOR1 and TOR2 (shaded). Structures depict the MAS-B1 element within Cryo-EM structures of TORC2 (left) (Karuppasamy et al., 2017) and mTORC2 (right) (Scaiola et al., 2020). The four amino acids shaded in the alignment are highlighted in red in both structures.