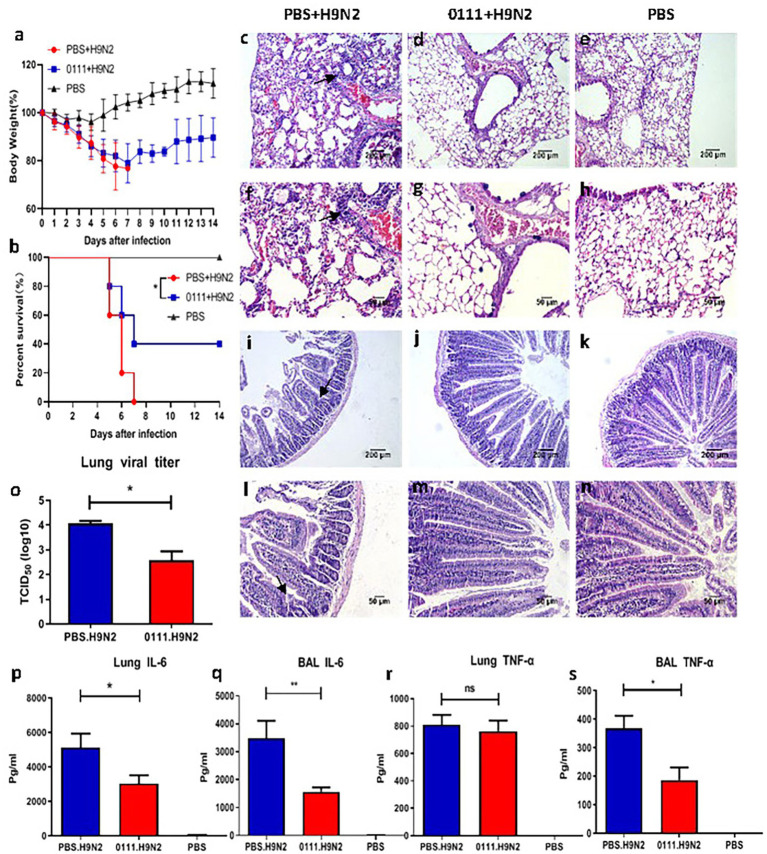
Figure 1.
Pretreatment of C57BL/6 mice with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 0111 reduced weight loss, improved survival and reduced lung and jejunum tissue damage as well as reduced lung viral load and inflammatory cytokines caused by H9N2 influenza virus infection. C57BL/6 mice (n = 5/group) were infected 7 days after the continuous oral administration of H9N2 virus (2 x LD50) by L. plantarum 0111 (1 × 108 CFU/200 glimouse). The body weight (A) and survival rate (B) of the mice are recorded within 14 days after infection. On day 5 after infection, some mice were euthanized, and the lungs and jejunum were collected and histologically analyzed. Lung viruses and inflammatory cytokines were measured in the lungs and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). (C,D,E,I,J,K) magnification at 100×. The scale bar indicates 200 μm. (F,G,H,L,M,N) magnification at 200×. The scale bar indicates 50 μm. (C,F) the lungs of mice were challenged with H9N2 after PBS pretreatment; (D,G) the lungs of mice were challenged with H9N2 after L. plantarum 0111 pretreatment; (E,H) the lungs of mice were challenged with PBS only. (I,L) mouse jejunum challenged with H9N2 after PBS pretreatment; (J,M) mouse jejunum challenged with H9N2 after L. plantarum 0111 pretreatment; (K,N) mouse jejunum treated with PBS only. (O) pulmonary virus log10TCID50/g lung tissue. (P) IL-6 (pg/ml) in lungs. (R) TNF-α (pg/ml) in lungs. (Q) IL-6 (pg/ml) in BALF. (S) TNF-α (pg/ml) in BALF. The results are presented as the means ± SEMs (N = 5), and statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.