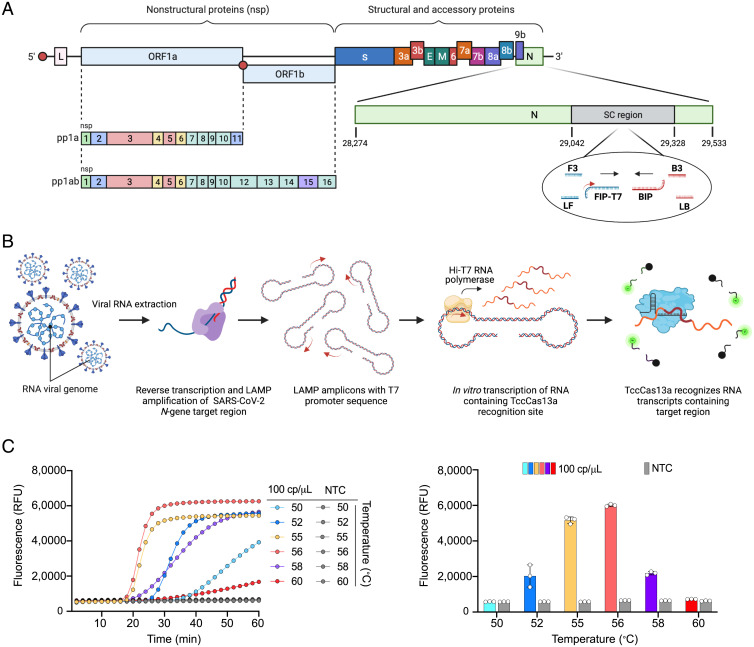
Fig. 4.
Establishment and optimization of one-pot SARS-CoV-2 detection using the thermophilic TccCas13a protein. (A) Schematic representation of the SARS-CoV-2 genome showing the region targeted by RT-LAMP amplification and the crRNA target sequence. The small red arrow on the T7-FIP primer indicates the T7 promoter sequence. SC region: genomic region of SARS-CoV-2 N gene targeted with STOPCovid primers. (B) Overview of the assay workflow. The detection protocol consists of three distinct steps, all carried out in the same tube and at the same temperature (56 °C). Following the extraction of viral RNA, specific target sequences within the viral RNA undergo RT into complementary DNA and are amplified with RT-LAMP isothermal amplification using LAMP primers containing the T7 promoter sequence (small red arrow on the T7-FIP primer). The resulting RT-LAMP amplicons are used for in vitro transcription using the thermostable Hi-T7 RNA polymerase, producing RNA transcripts that are recognized and targeted simultaneously by the thermophilic TccCas13a protein. Recognition of the RNA transcripts by TccCas13a triggers Cas13 collateral cleavage activity, resulting in trans cleavage of the reporter probe conjugated to the HEX or FAM fluorophores. (C) Performance of one-pot detection assay at different temperatures. (Left) As determined by real-time fluorescence at a given target RNA concentration (100 cp/μL); data are shown as mean (n = 3). (Right) End-point fluorescence signal measured after 30 min; values are shown as mean ± SD. The best performance was achieved at 56 °C. NTC, no template control; RFU, relative fluorescence unit.