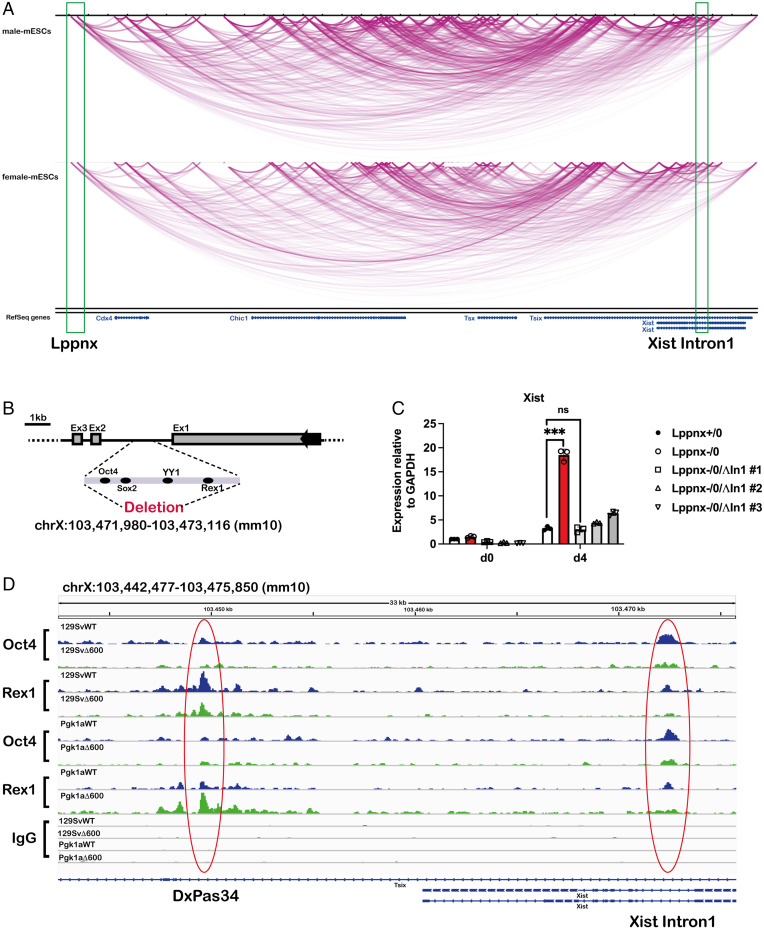
Fig. 5.
The Lppnx locus may interact with Xist Intron1 in mouse ES cells and controls the loading of Oct4 and Rex1 in XI1. Screenshot of a Hi-C analysis showing a part of the X inactivation center including Xist and Lppnx. The green rectangles indicate the transcription start site of Lppnx and Xist Intron1 showing a possible interaction between these two regions in both, male and female ES cells (A). Schematic view of the pluripotency factor binding region of Xist intron 1 which was deleted in 129Sv and 129SvΔ600 male ES cells, respectively, using CRISPR (B). Elevated Xist expression observed in 129SvΔ600 male ES cells (Lppnx-/0) after differentiation is completely reversed after the deletion of Xist Intron1. Three independent lines (#1, #2, #3) are shown. Two-sample t test P = 0.001 (C). Lppnx regulates the loading of pluripotency factors in Xist Intron1 and DxPas34. ChIPseq experiments show that upon deletion of Lppnx the loading of Oct4 and Rex1 is reduced at Xist Intron1 (red circle, Right) in male 129Sv and Pgk1a ES cells. In contrast, Rex1 binding at DxPas34, a regulatory region of Tsix, is reduced in Lppnx-deficient 129Sv ES cells, whereas in Pgk1a cells Rex1 binding is increased (red circle, Left) (D).