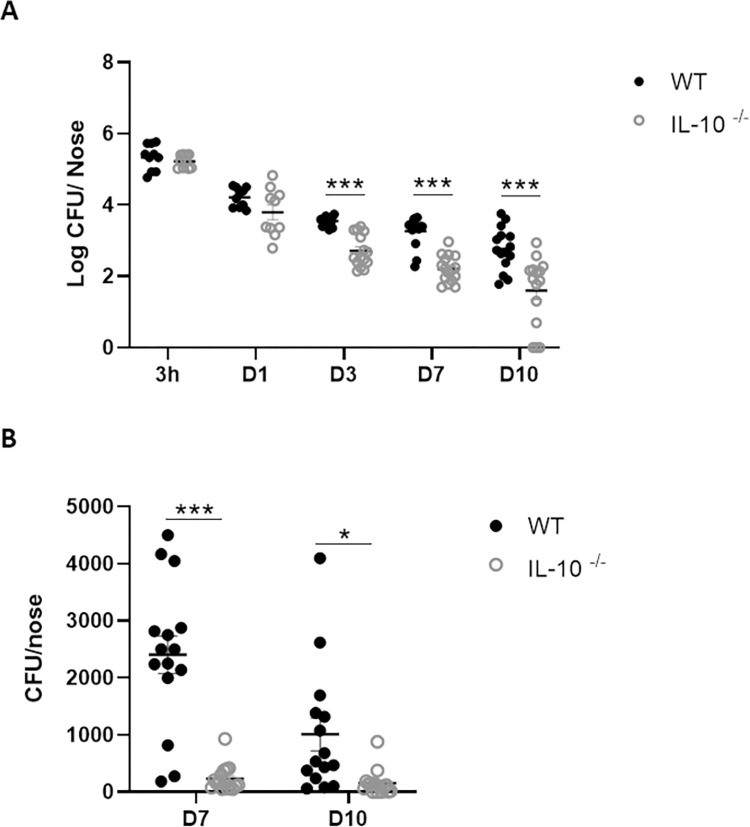
Fig 2. Bacterial burden is significantly reduced in the nasal cavity of IL-10-/- mice during S. aureus nasal colonisation.
Wild-type and IL-10-/- mice were intranasally colonised with S. aureus Newman SmR (2 × 108 colony-forming units/nose). At 3h, 1 day, 3 days, 7 days and 10 days mice were culled and noses were excised. Noses were homogenized and serial dilutions of homogenates were plated onto streptomycin-supplemented TSA plates. Plates were grown overnight and CFUs were enumerated. Results are expressed as Log CFU/nose (A) (Experimental unit = 1 mouse, n = 10–16 animals per time point, total # animals used 133, data pooled from 3 independent experiments). Day 7 and Day 10 data are also depicted as CFU/nose (B). Statistical analysis was carried out by one-way ANOVA, and student t-test. *P≤0.05; *** P≤0.001.