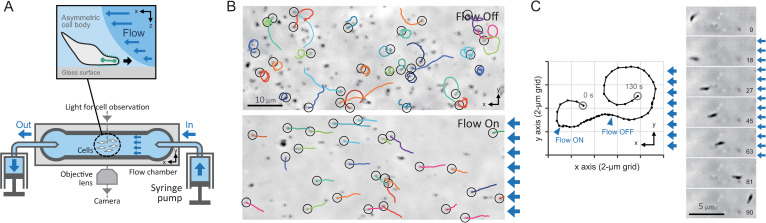
Fig 1. Rheotactic behavior of M. pneumoniae.
(A) Experimental setup. Cells were poured into a flow chamber connected to a syringe pump. Precisely controlled fluid flow was applied from the right side in the following images, and the cell behaviors were observed under phase-contrast microscopy. Left upper: Schematic of positive rheotactic behavior. A cell adheres to the glass surface at the attachment organelle and moves over the surface in an upstream direction against the fluid flow. (B) Field image of the rheotactic behavior. Cell trajectories for 40 s (color lines) are plotted on the phase-contrast images. The start position of a trajectory is marked by the black circle. The blue arrows on the right side of the image represent the direction of the fluid flow. Upper: No fluid flow. Lower: Fluid flow at 1.7 mm/s. (C) Single-cell trajectory. Left: Moving trace at 2-s intervals. Arrowheads indicate cell positions at the start and the end of fluid flow. Right: Time-lapsed image. Each time point is presented at the bottom right of the image.