Fig. 1. Potency, escapability, and breadth of a panel of RBD antibodies.
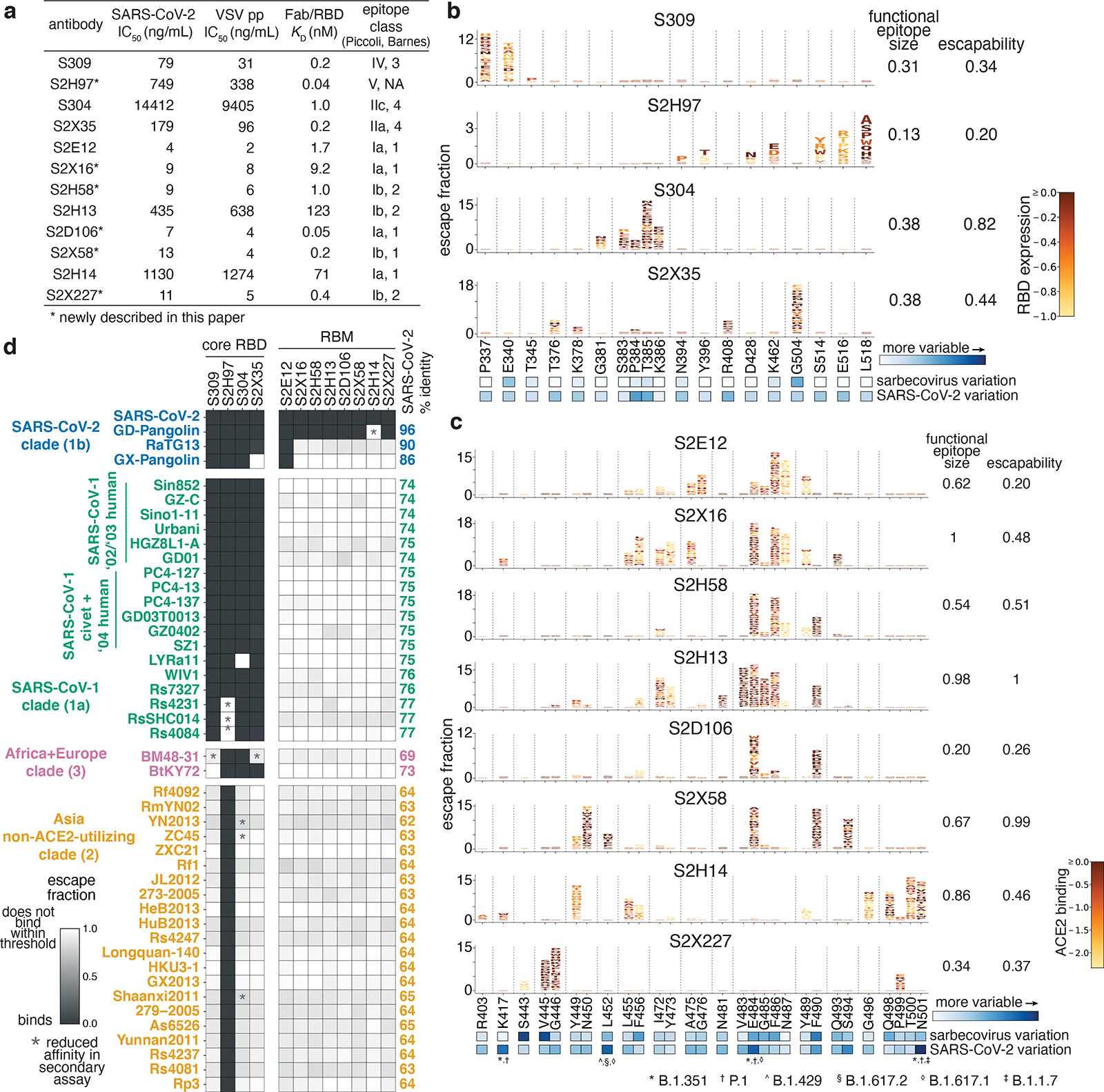
a, SARS-CoV-2 neutralization potency (authentic virus [n=3] and spike-pseudotyped VSV particles [n = 3 to 8] on Vero E6 cells), Fab:RBD binding affinities measured by SPR [n = 2 to 4], and epitope classifications. Additional details in Extended Data Table 1. b,c, Deep mutational scanning maps of mutations that escape binding by antibodies targeting the core RBD (b) or the receptor-binding motif (c). Letter height indicates that mutation’s strength of escape from antibody binding. Letters colored by effect on folded RBD expression (b) or ACE2 binding affinity (c)26. Relative “functional epitope size” and “escapability” are tabulated at right, scaling from 0 (no escape mutations) to 1 (largest epitope/most escapable antibody). Heatmaps, bottom, illustrate variability among sarbecovirus or SARS-CoV-2 sequences. d, Antibody binding to a pan-sarbecovirus RBD panel. Heatmap illustrates binding from FACS-based selections (scale bar, bottom left). Asterisks, reduced-affinity binding in secondary binding assays (Extended Data Fig. 4a–f).
