Extended Data Fig. 2. Deep mutational scanning to map mutations that escape antibody binding.
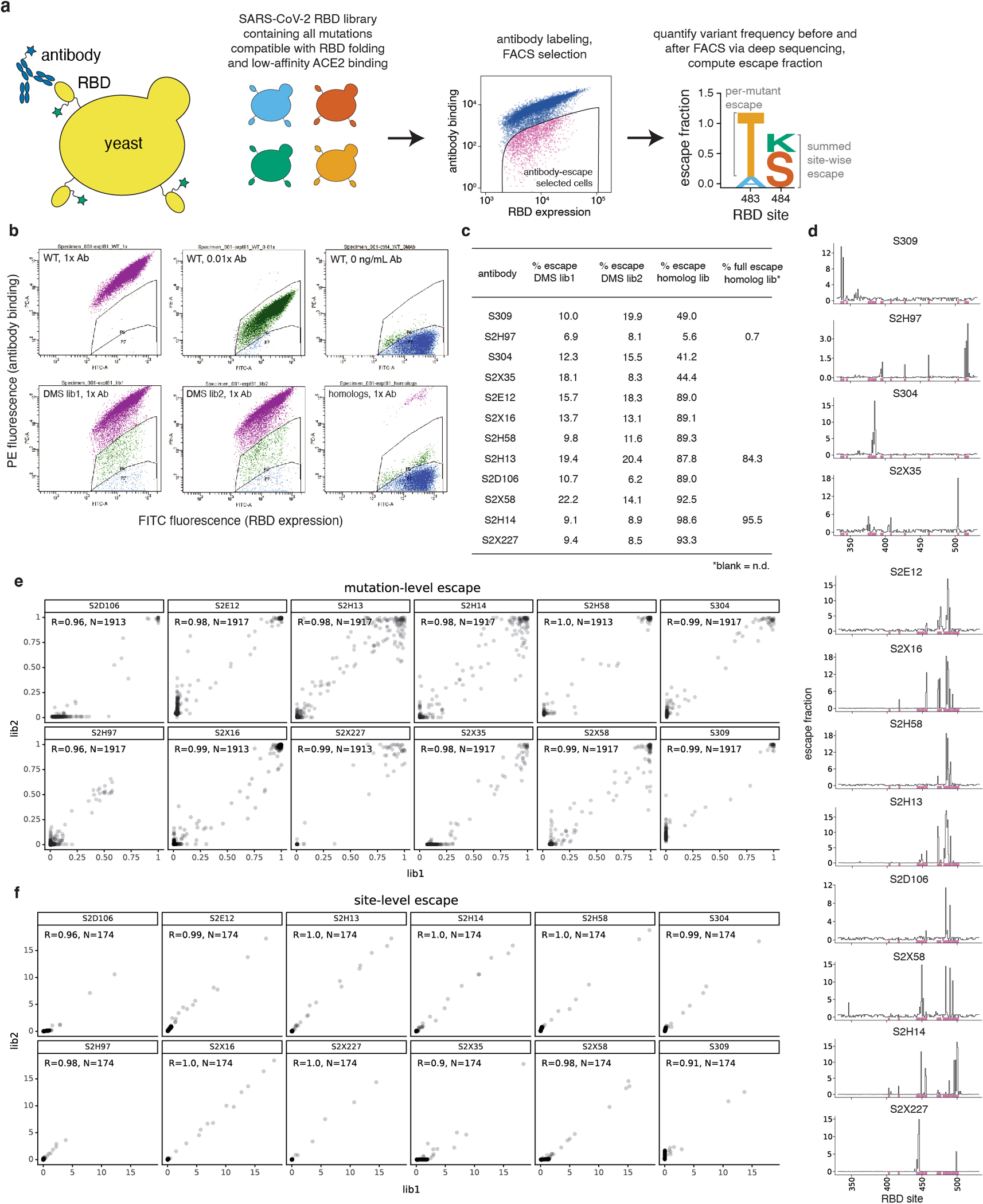
a, Scheme of the deep mutational scanning assay. Conformationally intact RBD is expressed on the surface of yeast, where RBD expression and antibody binding is detectable via fluorescent labeling. We previously constructed mutant libraries containing virtually all of the 3,819 possible amino acid mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RBD26 and sorted the library to eliminate mutations that destabilize the RBD or strongly reduce ACE2-binding affinity3. We incubate the library with a sub-saturating antibody concentration and use fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) to isolate yeast cells expressing RBD mutants with reduced antibody binding. Deep sequencing quantifies mutant frequencies before and after FACS selection, enabling calculation of the “escape fraction” of each amino acid mutation, which reflects the fraction of cells carrying that mutation that fall into the antibody-escape bin. Mutation escape fractions are represented in logoplots, where the height of a letter reflects the extent of escape from antibody binding. b, Representative selection gates, after gating for single cells expressing RBD as in Greaney et al.3. Yeast expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RBD (top panels) are labeled at 1x, 0.01x and no antibody to guide selection gates. Mutant RBDs that reduce binding (green, gate drawn to capture 0.01x WT control) are sorted and sequenced for calculation of mutant escape fractions. This same gate was used to quantify escape within libraries of yeast expressing all sarbecovirus RBD homologs. For several antibodies, we also selected the sarbecovirus RBD library with a more stringent “full escape” gate (blue, gate drawn to capture 0 ng/mL WT control). c, Fraction of library cells falling into escape bins for each antibody selection. d, Line plots showing total escape at all RBD sites for each antibody. Sites of strong escape illustrated in logoplots in Fig. 1b,c shown with pink indicators. e,f, Correlation in per-mutation (e) and per-site (f, sum of per-mutation) escape fractions for duplicate libraries that were independently generated and assayed. N, number of mutations (e) or sites (f) in the correlation.
