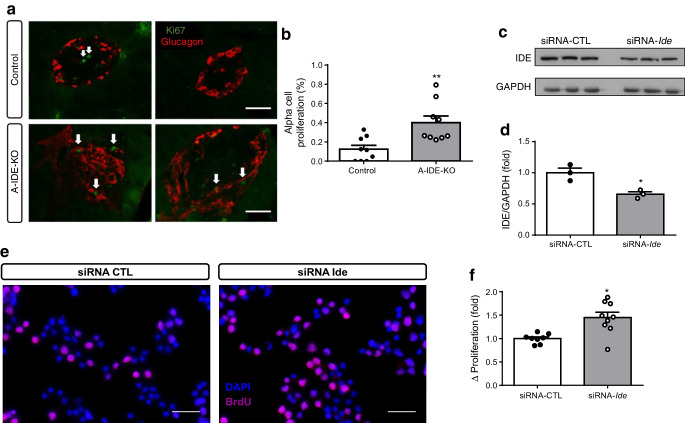
Fig. 7.
Deletion of IDE triggers alpha cell proliferation. (a) Representative images of Ki67 (green) and glucagon (red) staining in A-IDE-KO and control mouse pancreases. Scale bar, 40 μm. Arrows point to proliferative/Ki67-positive cells. (b) Quantification of alpha cell proliferation by Ki67/glucagon cells per total number of glucagon cells (n = 9). (c, d) IDE-knockdown in alpha-TC1.9 cells using siRNA-Ide or siRNA-CTL (scrambled control), showing a ~40% decrease in IDE expression (n = 3). (e) Representative images of BrdU staining in IDE-deficient and control alpha-TC1.9 cells. Scale bar, 100 μm. (f) Quantification of proliferation by detection of BrdU-positive cells (n = 9). Data are presented as means ± SEM. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 vs control mouse or vs siRNA-CTL treatment