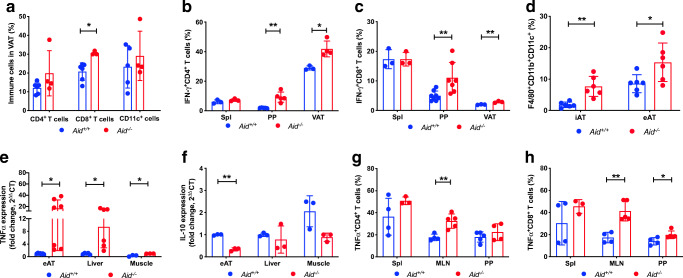
Fig. 2.
Aid−/− mice have increased proinflammatory immune infiltration in VAT and mucosal lymph nodes. Six-week-old male Aid+/+ or Aid−/− mice were fed HFD for 16 weeks prior to termination. (a) The proportion of immune-infiltrating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and CD11c+ cells from VAT were determined by flow cytometry and gated from live single cells. (b, c) Cells from the spleen, PP and VAT were harvested and stimulated for 4 h in the presence of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), ionomycin and GolgiPlug (BD Biosciences), prior to cell staining. The proportion of IFN-γ-producing CD4+ T cells (b) and IFN-γ-producing CD8+ T cells (c) gated as in a. (d) The proportion of macrophages in the inguinal and epididymal adipose tissue, gated from live, single CD11b+CD11c+F4/80+ cells. (e, f) Adipose tissue, liver and muscle were snap-frozen, prior to RNA extraction and qPCR for Tnfα (also known as Tnf) (e) and Il-10 (also known as Il10) (f) gene expression analysis. Samples were averaged from triplicates with the relative gene expression determined using the method by normalisation with the housekeeping gene, Gapdh. (g, h) The proportion of TNF-α-secreting CD4+ (g) and CD8+ (h) T cells from the spleen, MLN and PP, investigated by flow cytometry and gated as in a. Data are pooled from two independent experiments, except for e and f, which show one representative of two experiments (n = 3–6). Data were assessed for significance using Student’s t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. eAT, epididymal adipost tissue; iAT, inguinal adipose tissue; Spl, spleen