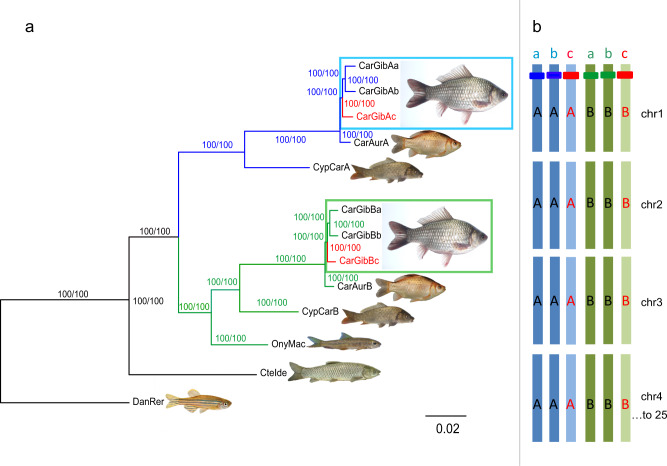
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic relationships and subgenome structure.
a Phylogenies using maximum likelihood (ML) based on chromosome-wide alignments (coding and non-coding sequence) of each of the 6 × 25 haplotypes of the C. gibelio hexaploid genome. Its haplotypes (CarGib_Aa, _Ab,_Ac, _Ba, _Bb, _Bc) are shown in comparison to collapsed chromosome-scale data of the ancestral diploid cyprinid grass carp (CteIde), and the diploid cyprinid Onychostoma macrolepis (OnyMac), allotetraploid common carp, Cyprinus carpio (CypCar), allotetraploid Carassius auratus (CarAur), and diploid zebrafish (DanRer). Note the slight difference in branch lengths for the subgenomes A vs. B. The tree was calculated from a genome-wide concatenation of the data analyzed for the 25 single trees and the addition of zebrafish as outgroup (in total 183.5 Mbp alignment length corresponding to 20.8% of the Onychostoma macrolepis reference chromosomes; gap content comprised 9.8%). Values for Shimodaira–Hasegawa approximate likelihood ratio tests and ultrafast bootstrap support (SH-aLRT [%]/UFB [%]) methods are given at each node, where 100/100 presents the percentage of bootstrap support. Note that due to methodology, Aa and Ab are collapsed to CypCar_A and CarAur_A as well as Ba and Bb are collapsed to CypCar_B and CarAur_B, respectively. b Subgenome structure of the formally hexaploid Prussian carp (C. gibelio) genome. The two subgenomes A and B, each with three haplotypes a, b, c (above), symbolize chromosome sets of the two diploid ancestral species (AaAb and BaBb, each with 25 chromosomes), which gave rise to the allotetraploid common ancestor (AaAbBaBb) of the Carassius and Cyprinus lineage by an ancient hybridization event. The Prussian carp arose by an autopolyploid addition of two chromosome sets (AcBc) and thus contains 150 (= 6 × 25) chromosomes. Blue or green (a, b) and red (c) bars represent homologous alleles (among homologous haplotypes a–c: blue or green) and homeologous alleles (between subgenomes A or B: blue vs. green).