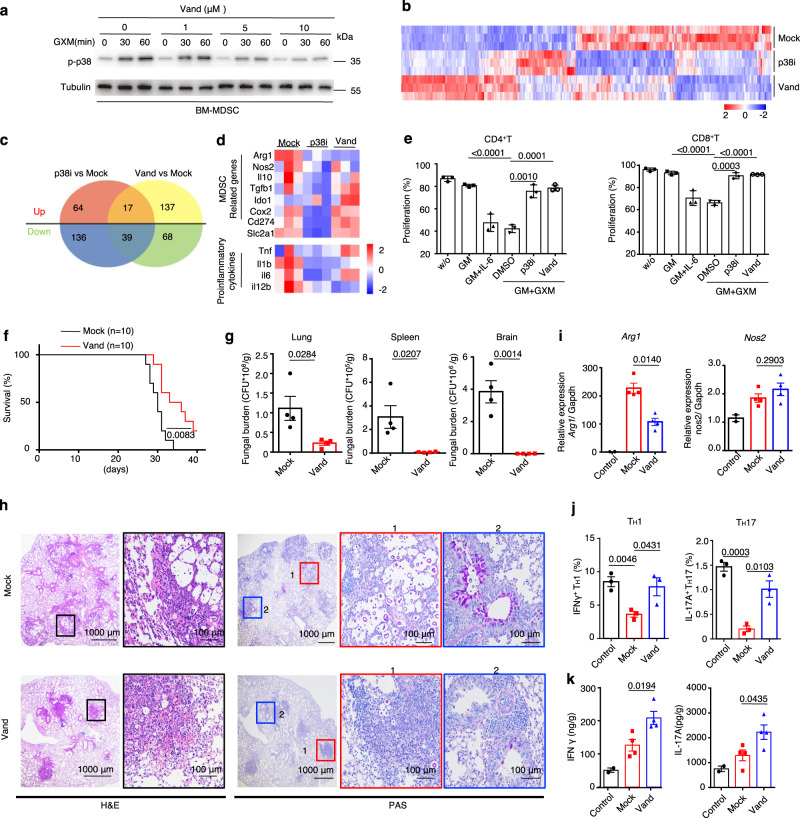
Fig. 6. Vandetanib inhibits MDSC-derived arginase-1 production to enhance T-cell-based immunotherapy against C. neoformans infection.
a Western blot assay of phosphorylated p38 in BM-derived MDSCs, which were generated by GM-CSF (40 ng/ml) + GXM (10 μg/well) for 5 days and then treated with GXM (10 μg/well) combined with vandetanib at the indicated concentration and time, Tubulin (55 kDa) served as a loading control. Representative blots were shown from three independent experiments. b–d Heatmap (b) and Venn diagram (c) of all differentially expressed genes, and heatmap of differentially expressed MDSC-related and pro-inflammatory genes (d) in wild-type BM-derived MDSCs, which were generated by GM-CSF (GM, 40 ng/ml) + GXM (10 μg/well) and then treated with GXM (10 μg/well) combined with p38 inhibitor SB202190 (p38i, 10 μM) or vandetanib (Vand, 5 μM) for 3 h. e Proliferation frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells, which were co-cultured with wild-type BM-derived MDSCs with or without treatment of p38 inhibitor SB202190 (p38i, 10 μM) or vandetanib (Vand, 5 μM) for 72 h. f Survival assay of C. neoformans strain H99-infected mice (n = 10, 1 × 103 CFU/mouse), which were intraperitoneally treated with or without vandetanib (Vand, 50 mg/kg every other day). g–k Fungal burden in lung, spleen and brain on Day 21 (g), representative histological images with hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) and Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) staining (h), mRNA levels of Arg1 and Nos2 (i), the frequency of IFNγ+ TH1 and IL-17A+ TH17 cells (j), and the amount of IFN-γ and IL-17A (k) in the lungs of C. neoformans strain H99-infected mice (1 × 103 CFU/mouse) on Day 14, which were intraperitoneally treated with or without vandetanib (Vand, 50 mg/kg every other day). Scar bars = 1000 μm (left) or 100 μm (right). Data were presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3 (e, j), n = 4 (g–i), and n = 10 (h) biologically independent samples. Data were analyzed by unpaired two-sided Student’s t-test in e, g–i, j, k and two-sided log-rank (Mantel–Cox) tests in f. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.