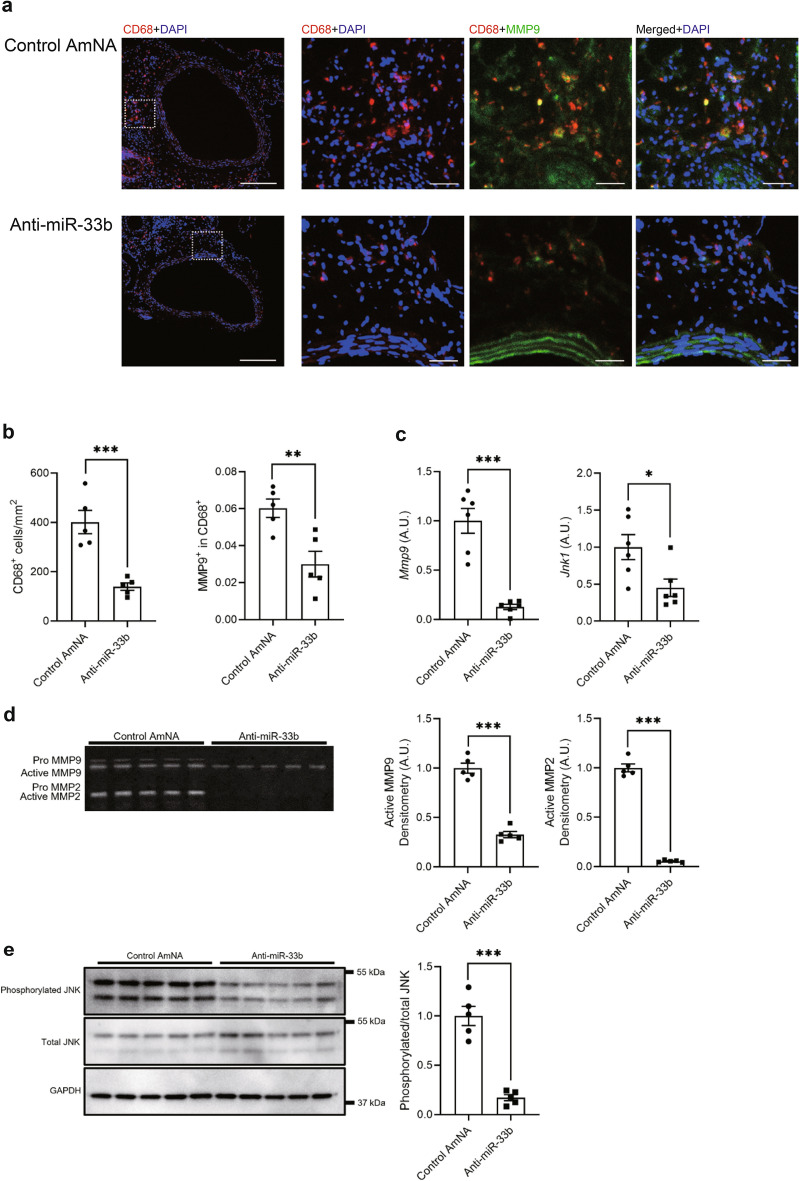
Figure 6.
Inhibition of miR-33b in miR-33b KI mice prevents accumulation of macrophages and attenuates the activities of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9). (a) Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for CD68 (red), MMP9 (green), and 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Scale bar indicates 200 µm for low power-field and 50 µm for high power-field. (b) Numbers of CD68-positive cells and quantification of CD-68/MMP9-double positive area in the sections of CaCl2-induced AAA wall, n = 5 in each group. Unpaired two-tailed t test. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. (c) Mmp9 and Jnk1 expression levels in CaCl2-induced AAA walls by quantitative real-time PCR, n = 6 mice in each group. Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (left) and unpaired two-tailed t test (right). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. (d) MMP9 and MMP2 activities of AMO-administered CaCl2-induced AAA walls were evaluated using gelatin zymography (left) and quantified using densitometric analyses (right), n = 5 mice in each group. Original gel is presented in Supplementary Fig. S4 online. Unpaired two-tailed t test (active MMP9 densitometry analysis) and unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (MMP2 densitometry analysis). ***P < 0.001. (e) JNK activity of AMO-administered CaCl2-induced AAA walls was assessed using western blotting (left) and quantified using densitometric analyses (right). GAPDH was served as an internal loading control, n = 5 mice in each group. Original blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S4 online. Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction. ***P < 0.001. All data represent mean ± SEM.