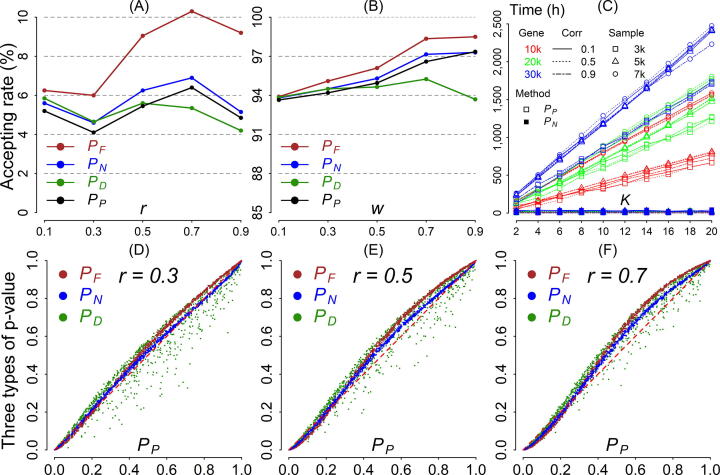
Fig. 1.
(A) Type I error for the p-value combination methods. The x-axis represents correlation . The y-axis represents Type I error. (B) Statistical power for the p-value combination methods. The x-axis represents correlation . The y-axis represents statistical power. (C) Computation time of the proposed method () and the permutation method (). The x-axis indicates number of thousand permutations (K). The y-axis indicates computation time. Red, green, and blue lines denote gene sizes G of 10,000, 20,000, and 30,000, respectively. The squares, triangles, and circles denote sample sizes N of 3,000, 5,000, and 7,000, respectively. Solid, dotted, and dot-dashed lines represent correlation coefficients of 0.1, 0.5, and 0.9, respectively. (D)–(F) Estimation accuracy of p-value. The x-axis represents the p-values of the benchmark method (). The y-axis indicates the p-values of the other p-value combination methods: , brown; , blue; , green). The results based on correlation coefficients 0.3, 0.5, and 0.7 are arranged from left to right.