Figure 2.
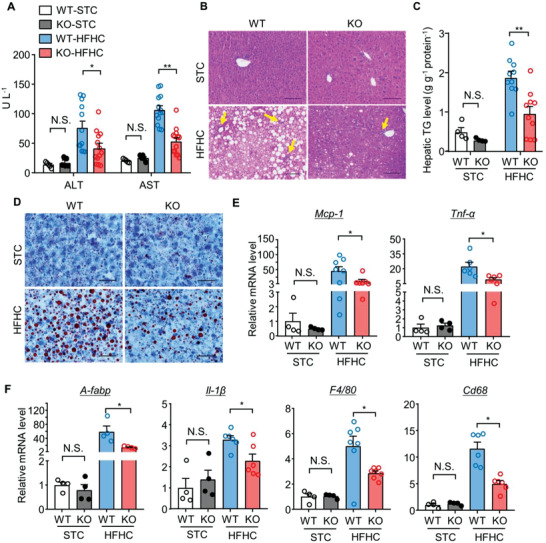
Hepatocyte‐specific deletion of MDM2 prevents diet‐induced hepatic steatosis and inflammation. 24‐week‐old male H‐MDM2‐KO mice and their WT littermates fed STC or HFHC diet were used. A) Serum levels of ALT and AST (n = 5 for the STC and n = 12–13 for the HFHC group). B) H&E staining of liver sections. Yellow arrows indicate immune cell clusters. (Scale bar: 100 µm). C) Hepatic triglyceride (TG) content normalized with protein concentration (n = 4 for the STC and n = 10 for the HFHC group). D) Oil‐red‐O staining of liver sections (scale bar: 100 μm). E,F) mRNA levels of E) Mcp‐1, Tnf‐α, F) A‐fabp, Il‐1β, F4/80, and Cd68 normalized with 18s in livers (n = 4 for STC and n = 4–8 for HFHC groups). The mRNA levels are expressed as fold change over WT‐STC. Representative histological images are shown. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. (U test for STC in panel C), and Tnf‐α in panel E), and A‐fabp, F4/80 in panel F); Welch's t‐test for Mcp‐1 in panel E) and Cd68 in panel F); two‐tailed independent Student's t‐test for the remaining data). Not statistical significance (N.S.).
