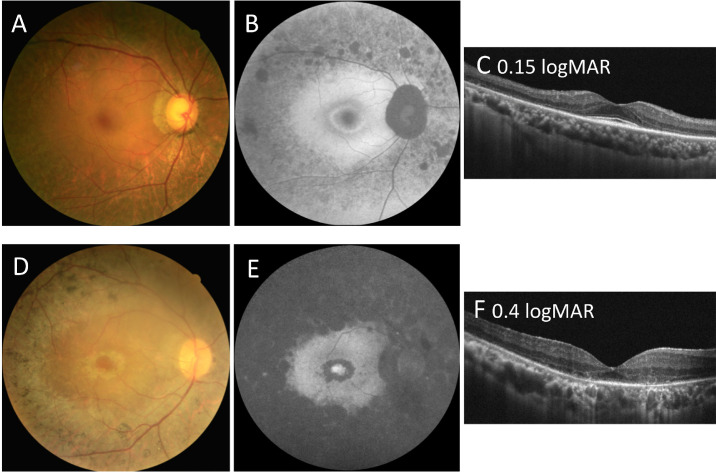
Figure 4.
Comparison of fundal imaging findings among patients with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa carrying eyes shut homolog (EYS) gene variants at different locations. (A, B, C) Color fundus photograph and fundus autofluorescence (FAF) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging results for a 63-year-old man (patient ID: P32) carrying the c.2276G>A and c.6416G>A variants, showing a relatively normal visual acuity of 0.15 logMAR. He was classified as group B for the genetic subgroup and as pericentral-type RP for the phenotypic subtype. (B) FAF imaging showing the hypo-AF signal along the vascular arcades and hyper-AF circular patches inside the retinal arcade with a perifoveal hyper-AF ring. The far periphery is relatively spared. (C) OCT imaging showed the thinning of the outer retinal area and shortening of the ellipsoid zone line. The central macula region is relatively preserved. (D, E, F) Color fundus photograph and FAF and OCT imaging results for a 40-year-old man (patient ID: P26) carrying the c.6416G>A and c.8012T>A variants, showing mild visual impairment of 0.4 logMAR. He was classified as group C for the genetic subgroup and as typical-type RP for the phenotypic subtype. (E) FAF imaging showing the near absence of autofluorescence outside, but hyper-AF circular patches inside, the retinal arcade. There was also an increased AF signal in the fovea region. (F) OCT imaging showed the thinning of the outer retinal area and the loss of a discernible ellipsoid zone line.