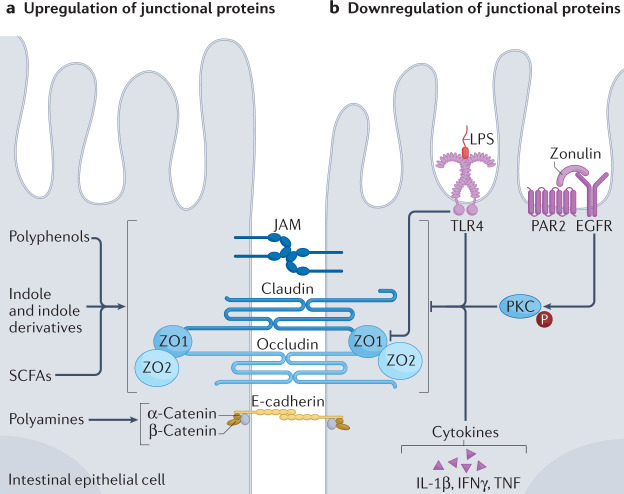
Fig. 2. Mechanisms of gut permeability-mediated low-grade endotoxaemia.
The gut epithelial barrier consists of the apical plasma membrane of enterocytes, held together by tight junction proteins (claudin and occludin) and adherens junction proteins (E-cadherin and catenin), as well as the zonula occludens proteins ZO1 and ZO2, which are adaptor proteins necessary for the structural and regulatory functions of tight junctions. a | Upregulation of junctional proteins can be induced by microbiota metabolites including polyphenols, indole and indole derivatives, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and polyamines. b | Downregulation of junctional proteins is mediated by: lipopolysaccharides (LPS) through binding to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4); by zonulin, a protein that activates the EGF receptor (EGFR) through transactivation of the proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2), thereby inducing protein kinase C (PKC) phosphorylation; and by pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, interferon-γ (IFNγ) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF). JAM, junctional adhesion molecules.