Figure 35.
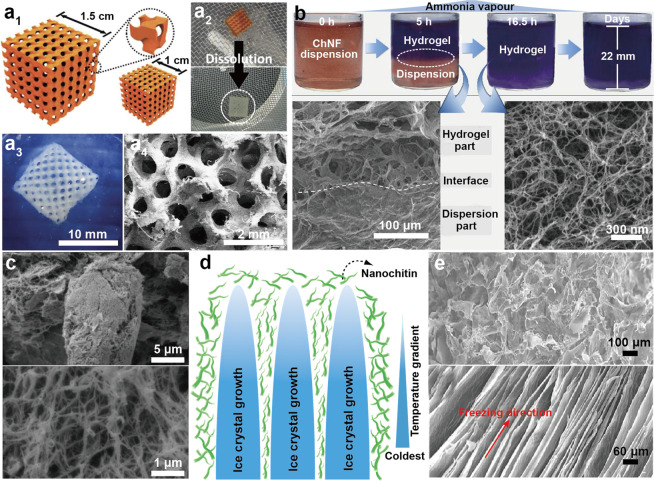
(a1) Structure of a scaffold used as a reverse template to form ChNF hydrogels. (a2) Visual appearance of the dissolution in alkaline media of the sacrificial template to form the ChNF hydrogel. (a3) Photograph and (a4) SEM image of ChNF hydrogel scaffold with a 10 mm edge length. Adapted with permission from ref (618). Copyright 2015 John Wiley and Sons. (b) Gelation process involving ChNFs in the presence of ammonia vapor during given processing time. Following a limited gelation period (5 h), a clear interface between the upper hydrogel phase and the bottom dispersion phase coexists (SEM image, bottom left); after ChNF dispersion is fully gelled (16.5 h), a network structure is formed by the nanofibers (SEM image, bottom right). Adapted with permission from ref (621). Copyright 2020 Springer Nature. (c) SEM images at higher magnification of a ChNC aerogel where the upper panel shows a porous network and nanocrystal aggregation with the bottom panel showing a highly porous network. Adapted with permission from ref (614). Copyright 2013 John Wiley and Sons. (d) Schematic illustration of the directional freezing used to prepare nanochitin cryogels. (e) SEM images of the cross section of freeze-dried ChNF cryogels, with the upper and bottom panels indicating ChNF cryogels obtained by freezing at −80 °C and under liquid nitrogen, respectively. Adapted rom ref (554). Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society.