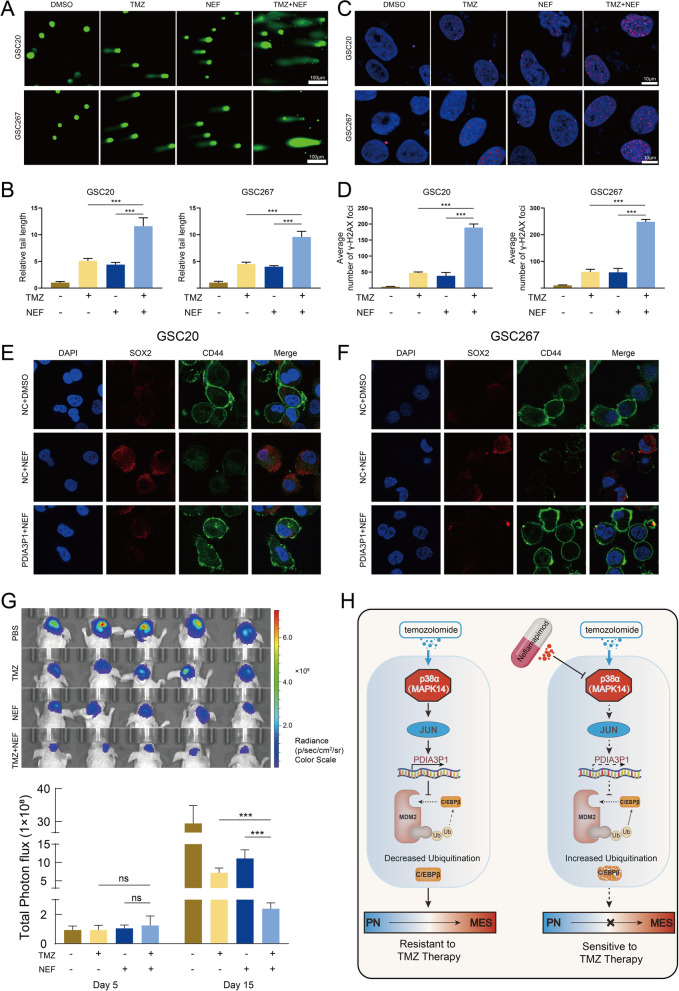
Fig. 7.
NEF combined with TMZ confers a better anti-tumor effect both in vitro and in vivo. A B The representative images (A) and quantification (B) of comet assay showed that TMZ (400 μM, 48 h) combined with NEF (50 μM, 48 h) contributed a stronger DNA damage effect in GSC20 and GSC267, respectively. Scale bar, 100 μm. C D The representative images (C) and quantification (D) of γ-H2AX staining in GSC20 and GSC267 (TMZ 400 μM, 48 h. NEF 50 μM, 48 h). Scale bar, 10 μm. E F Representative images of IF staining showed the effect of NEF treatment (50 μM, 48 h) and PDIA3P1 overexpression on the expression of CD44 and SOX2 in GSC20 (E) and GSC267 (F), respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm. G Bioluminescence imaging (upper panel) and quantification (lower panel) of tumor size in GSC267 xenografted nude mice treated with PBS, NEF (5 mg/kg, p.o., 5 days per week), TMZ (5 mg/kg, p.o., 5 days per week) or both drugs in combination. H Working model plot showing that PDIA3P1 plays a key role in promoting the TMZ resistance of GBM cells. The p38α-JUN was activated by TMZ treatment and promoting the transcription of PDIA3P1. PDIA3P1 disrupted the MDM2-C/EBPβ complex to stabilize C/EBPβ and promote PMT, thereby promoting the resistance of GBM cells to TMZ treatment. NEF, a highly selective p38α inhibitor, inhibited TMZ-induced upregulation of PDIA3P1 expression and provided a promising strategy to address the challenge of TMZ resistance in glioma cells