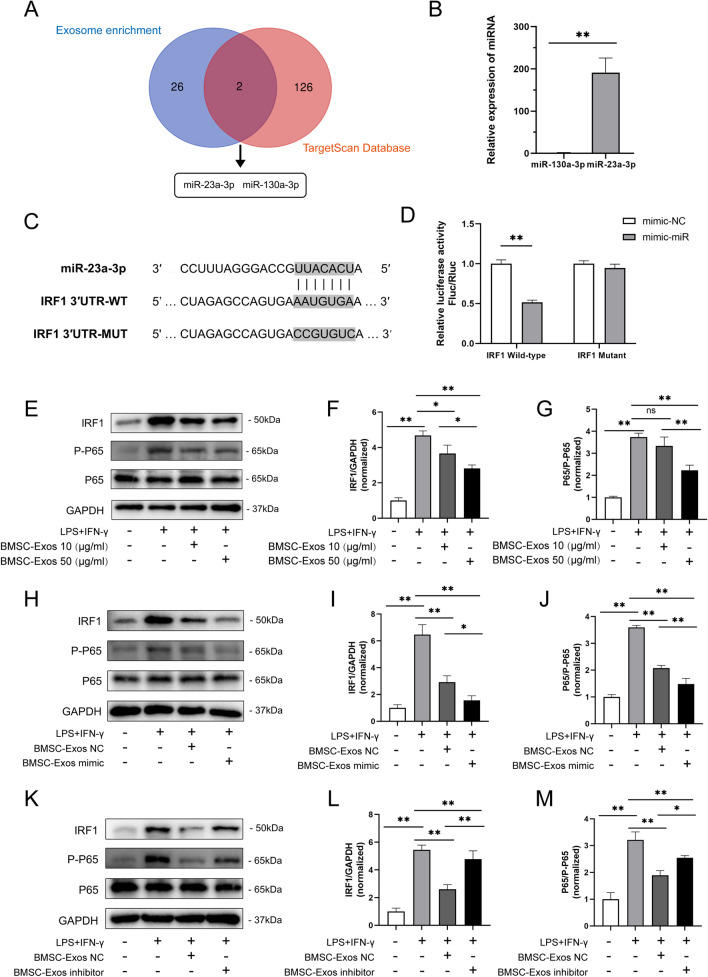
Fig. 3.
miR-23a-3p shuttling by BMSC-Exos modulates macrophage inflammation through targeting IRF1. A Venn diagram of the miRNA enriched in BMSCs and the miRNAs regulating IRF1. B The miRNA expression of miR-130-3p and miR-23a-3p in BMSC-Exos. The expression levels of the miRNAs were normalized to U6. n = 6. C The sequence of the wild-type or mutant seed region of IRF1 and the binding site of IRF1 mRNA with miR-23a-3p and the mutant 3′-UTR of IRF1. D 293T cells were co-transfected with luciferase reporter constructs containing wild-type/mutant 3′-UTR of IRF1 and miR-23a-3p NC/mimic for 24 h. The relative luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase luminescence. n = 6. E–G Protein levels of IRF1, P-P65, and P65 in LPS+IFN-γ-stimulated macrophages after being treated with 10 or 50 μg/ml BMSC-Exos for 48 h. n = 3. H–J Protein levels of IRF1, P-P65, and P65 in LPS+IFN-γ-stimulated macrophages after being treated with BMSC-Exos with miR-23a-3p mimic (BMSC-Exos mimic) or negative control (BMSC-Exos NC) for 48 h. n = 3. K–M Protein levels of IRF1, P-P65, and P65 in LPS+IFN-γ stimulated macrophages after being treated with BMSC-Exos with miR-23a-3p inhibitor (BMSC-Exos inhibitor) or BMSC-Exos NC for 48 h. n = 3. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed with Student’s t test and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.