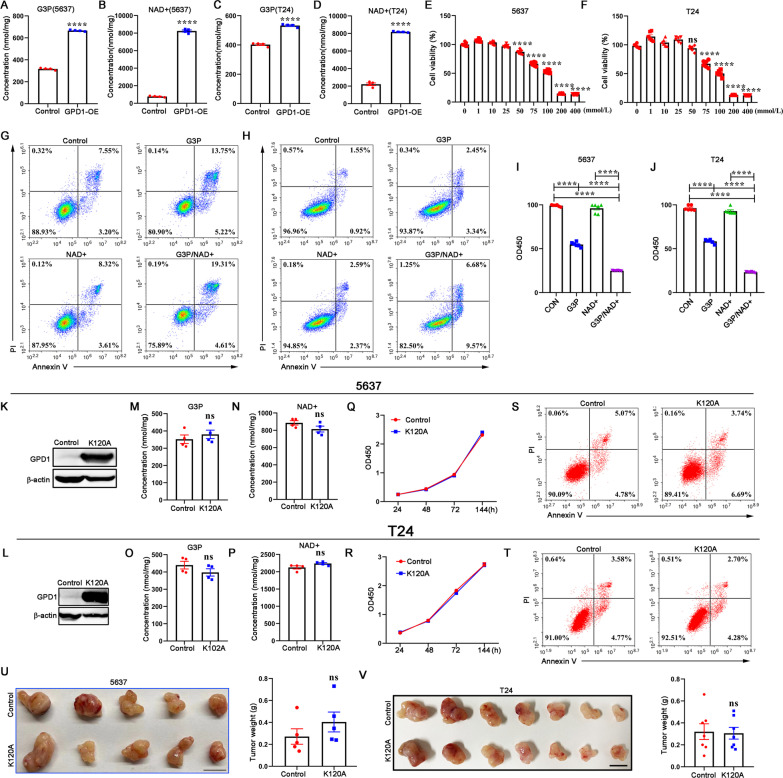
Fig. 3.
GPD1-induced inhibition of bladder cancer depends on its enzymatic activity. A and B Detection of intracellular G3P and NAD+ levels in control 5637 cells and GPD1-overexpressing 5637 cells. C and D Detection of intracellular G3P and NAD+ levels in control T24 cells and GPD1-overexpressing T24 cells. E and F CCK-8 assay to evaluate the proliferation of 5637 and T24 cells treated with different doses of G3P. G and H Flow cytometry analysis with Annexin V-PI staining was performed to evaluate the percentage of apoptotic 5637 cells and T24 cells treated with G3P or NAD+. I and J CCK-8 assay to evaluate the proliferation of 5637 and T24 cells treated with G3P or NAD+. K and L Western blotting to determine K120A GPD1 overexpression in 5637 and T24 cells. M and N Detection of intracellular G3P and NAD+ levels in control 5637 cells and K120A GPD1-overexpressing 5637 cells. O and P Detection of intracellular G3P and NAD+ levels in control T24 cells and K120A GPD1-overexpressing T24 cells. Q and R CCK-8 assay to evaluate the proliferation of K120A GPD1-overexpressing 5637 cells and T24 cells in vitro. S and T Flow cytometry analysis with Annexin V-PI staining was performed to evaluate the percentage of apoptotic cells in K120A GPD1-overexpressing 5637 and T24 cells. U Control 5637 cells or K120A GPD1-overexpressing 5637 cells were implanted in BALB/c Nude mice. Tumors were resected and measured 4 weeks later. V Control T24 cells or K120A GPD1-overexpressing T24 cells were implanted in BALB/c Nude mice. Tumors were resected and measured 4 weeks later