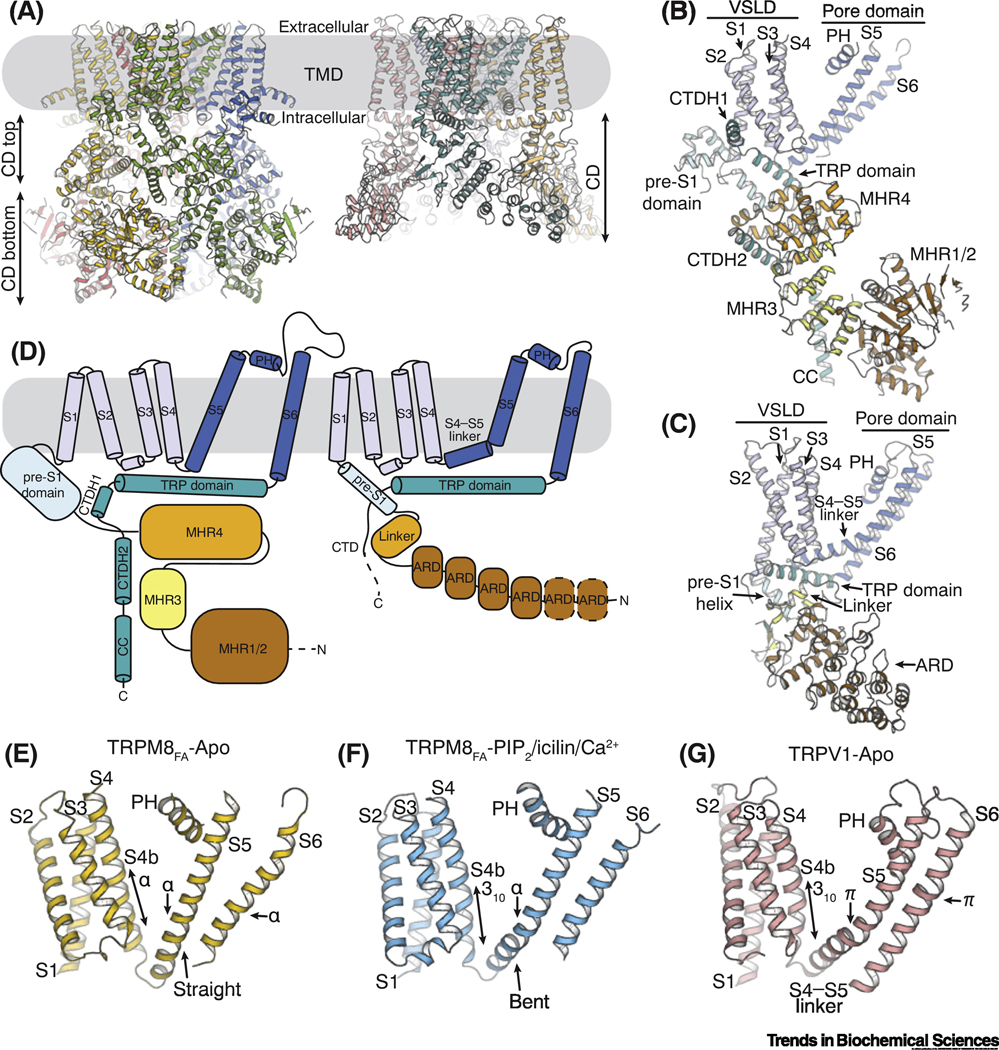
Figure 1. Unique structural features of TRPM8.
(A) Structure models showing the architecture of TRPM8 (left; PDB ID: 6BPQ) and TRPV1 (right; PDB ID: 3J5P) channels. The transmembrane domains (TMDs) are embedded in the plasma membrane (gray box). The cytoplasmic domain (CD) of TRPM8 can be further divided into the top (CD top) and the bottom (CD bottom) layers.
(B and C) Atomic models of a single protomer from TRPM8 (B) and TRPV1 (C), respectively. Abbreviations: ARD, ankyrin repeat domain; CC, coiled coil; CTDH, C-terminal domain helix; MHR, melastatin homology region; PH, pore helix; VSLD, voltage-sensor-like domain.
(D) Cartoon diagrams delineating the topology of TRPM8 (left) and TRPV1 (right). Subdomains labeled as in B and C.
(E-G) Comparison of the transmembrane domain (TMD) in the apo TRPM8FA (E,; PDB ID: 6BPQ), TRPM8FA in complex with PI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ (F; PDB ID: 6NR3), and the apo TRPV1 structures (G; PDB ID: 3J5P). The configurations of secondary structure in the C-terminus of S4 (S4b), S5, and S6 are indicated by arrows for comparison.