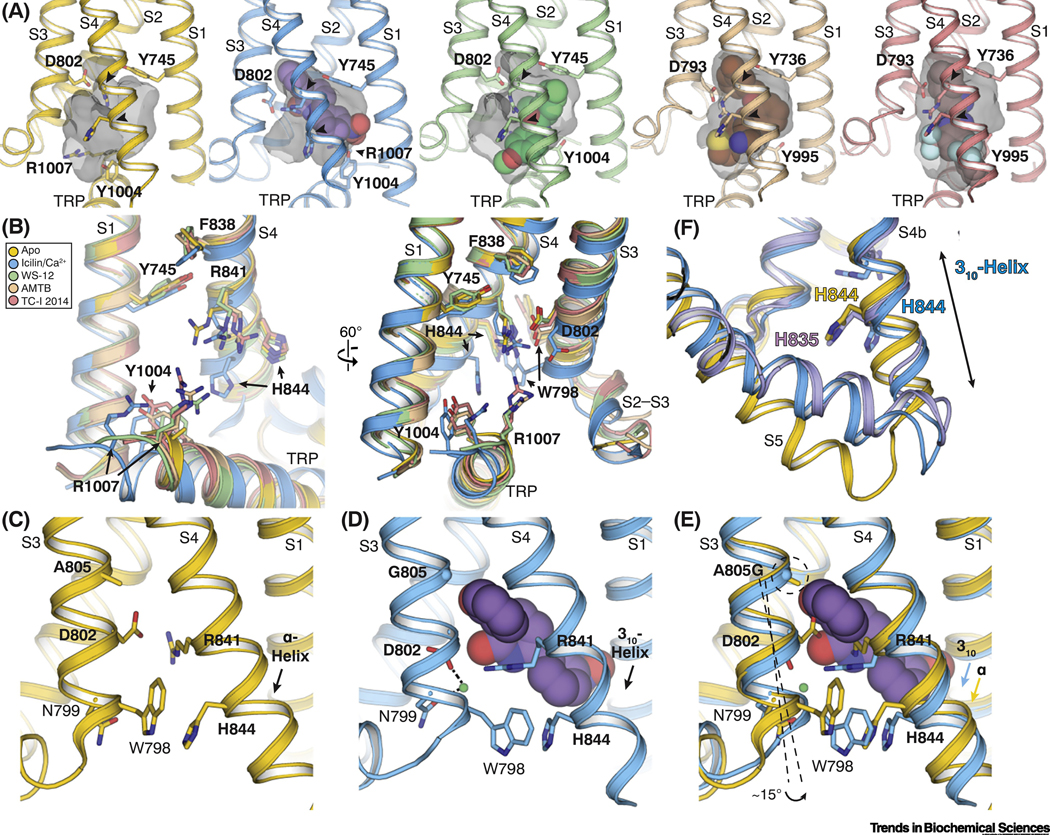
Figure 3. Molecular basis of ligand recognition by TRPM8.
(A) Comparison of the VSLD cavity in the TRPM8FA-Apo (yellow), TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ complex (blue), TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/WS-12 complex (green), TRPM8PM-AMTB complex (wheat), and TRPM8PM-TC-I 2014 complex (pink). Gray transparent surfaces represent the shape of the cavity mediated by residues lining the binding pocket. Arrowheads point the flexible arginine and histidine residues in S4 (R841 and H844 in TRPM8FA; R832 and H835 in TRPM8PM). Ligands are shown in spheres. PDB IDs indicated in Figure 2F legend.
(B) Overlay of the VSLD cavity in the ligand bound TRPM8 structures, showing the flexibility of the key ligand-binding residues. Color coding is the same as in (A). Residue numbering refers to TRPM8FA.
(C-E) Comparison of the VSLD cavity in the TRPM8FA-Apo (C, yellow) and the TRPM8FAPI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ complex (D, blue) structures, showing the conformational changes induced by icilin (purple spheres) and Ca2+ (green sphere) binding; especially S4b undergoes a α-to-310 helical transition. Superimposition of the two structures (E) suggests the Ca2+ coordination facilitates the icilin binding; the A805G mutation confers flexibility in S3 for the assembly of Ca2+ coordination and widens the VSLD cavity to accommodate the icilin molecule.
(F) Comparison of the ligand-induced conformational changes in S4 and S5 between TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ (blue) and TRPM8PM-Ca2+ structures (purple) with TRPM8FA-Apo (yellow). Ligand binding induces bending of S5 in TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ (blue) and TRPM8PM-Ca2+. The S4b in TRPM8PM-Ca2+ remains α-helical, whereas that in TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ transitions to a 310-helix.