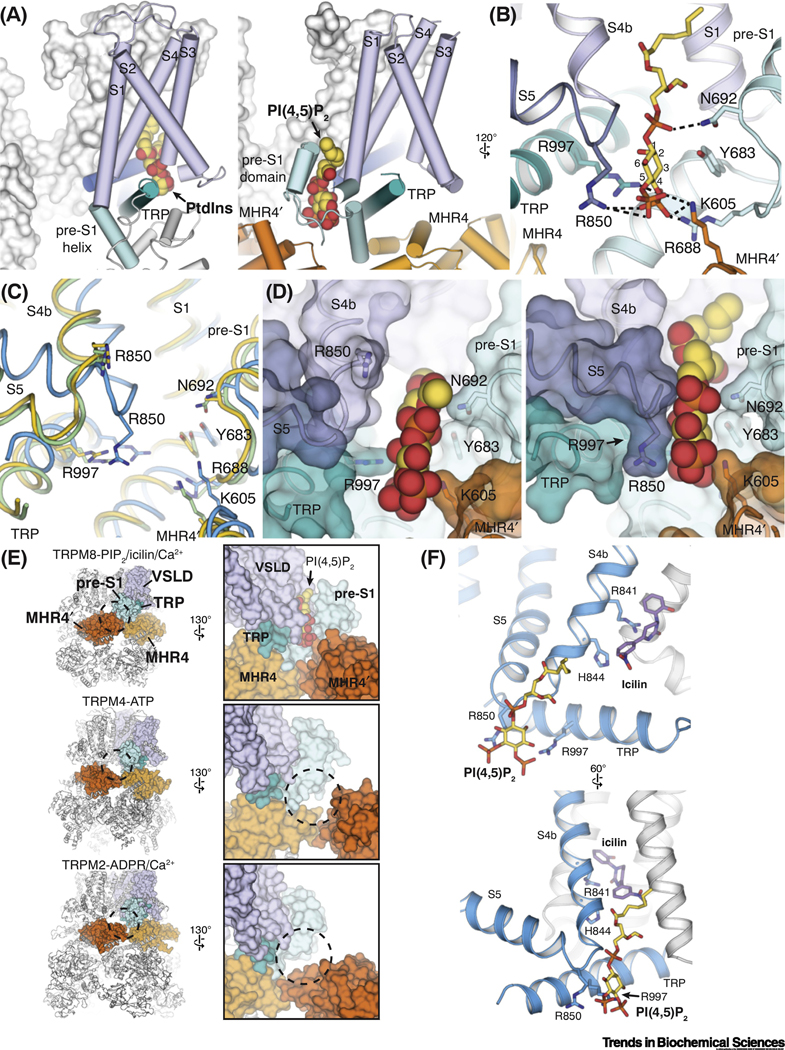
Figure 4. Structural basis of the PI(4,5)2 dependence of TRPM8.
(A) Comparison of the binding site for phosphatidylinositol lipid (PtdIns) (left; PDB ID: 5IRZ) in TRPV1 and that for PI(4,5)P2 in TRPM8 (right; PDB ID: 6NR3). Lipid molecules are shown as spheres.
(B) Residues interacting with PI(4,5)P2 (yellow sticks) in the interfacial cavity in TRPM8.
(C) Comparison of the PI(4,5)P2 binding site in TRPM8FA-Apo (yellow), TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ complex (blue), and TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/WS-12 complex (green). Structural rearrangements of S4 and S5 in the TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ complex reposition R850 closer to the PI(4,5)P2 binding site. PDB IDs indicated in Figure 2F legend.
(D) Surface representations showing two different conformations of the interfacial cavity which enable partially (left, TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/WS-12 complex) and fully (right, TRPM8FA-PI(4,5)P2/icilin/Ca2+ complex) engagement of PI(4,5)P2 with the TRPM8 channel. PI(4,5)P2 is shown in spheres.
(E) Global (left columns) and close-up (right columns) views comparing the intra- and inter-subunit domain interfaces in TRPM8 (PDB ID: 6NR3), TRPM4 (PDB ID: 5WP6), and TRPM2 (PDB ID: 6PUS). Tight association between the pre-S1 domain and the neighboring MHR4 domains contributes to the PI(4,5)P2 binding site in TRPM8.
(F) Distinct but adjacent binding sites for PI(4,5)P2 (yellow sticks) and icilin (purple sticks) (PDB ID: 6NR3) illustrate the allosteric coupling between the lipid and cooling agonists for TRPM8 activation.