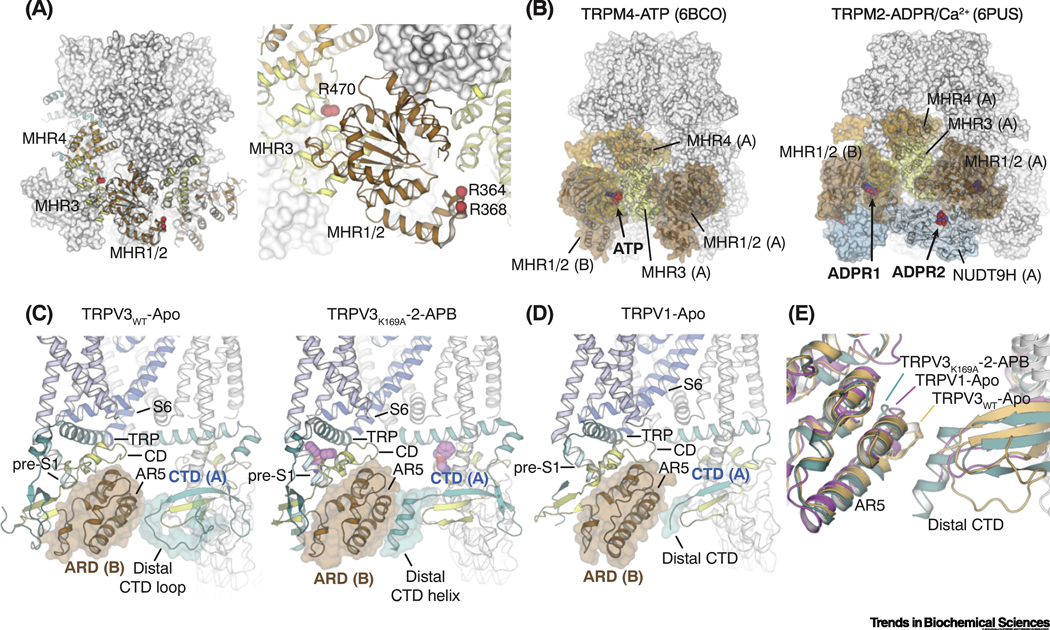
Figure 5. Regulatory functions of cytoplasmic domains in TRPM and TRPV channels.
(A) Residues in TRPM8 (red spheres) that have been implicated for direct interactions with Gαq mapped to the MHR1/2 and MHR3 domains.
(B) The ligand binding sites for ATP in TRPM4 (left; PDB ID: 6BCO) and ADP-ribose (ADPR) in TRPM2 (right; PDB ID: 6PUS) are located in the cytoplasmic domains of the channel.
(C) In TRPV3, state-dependent secondary structure changes from loop (left; PDB ID: 6MHO) to helix (right; PDB ID: 6OT5) in the distal C-terminal domain (CTD) triggers rearrangements in the inter-subunit interfaces, which are propagated to the TRP domain and lead to channel activation.
(D) Inter-subunit interface between the distal CTD and the neighboring ankyrin repeat domain (ARD) in the TRPV1-Apo structure (PDB ID: 3J5P).
(E) Structural comparison of the less-well defined CTD and ARD in the TRPV1-Apo with those in the closed and the open states of TRPV3. TRPV3WT-Apo: light orange, PDB 6MHO; TRPV3K169A-2-APB: teal, PDB 6OT5; TRPV1-Apo: magenta, PDB 3J5P.