Figure 2.
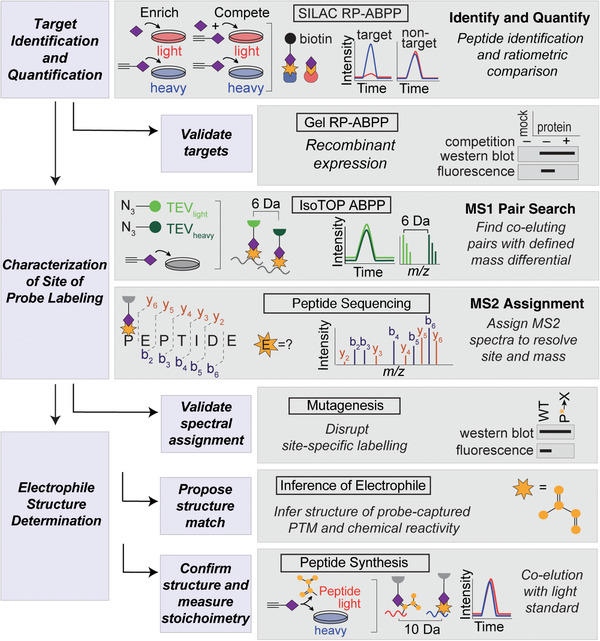
Schematic flowchart of RP‐ABPP experiments. Heavy (H) and light (L) cells, proteomes, and peptides are depicted in blue and red, respectively. Target identification and quantification is performed using SILAC RP‐ABPP extracted parent ion chromatograms and corresponding H/L ratios for tryptic peptides of probe targets quantified in enrichment and competition experiments. Targets are validated by gel RP‐ABPP western blots and RP‐ABPP data for hydrazine probe–treated transfected cells expressing a protein target. The first lane corresponds to a control transfection (“mock”) with the appropriate empty expression vector. The site of probe labeling is characterized using isoTOP ABPP experiments to determine coeluting isotopically differentiated peptide pairs and sequencing the ions to resolve the modified site. The site of probe labeling is validated through comparison of mutation and wild‐type (WT) probe‐labeling and expression profiles. The electrophile is determined, confirmed, and stoichiometrically quantified by inferring the electrophile and coelution of heavy‐Arg/Lys‐labeled transfected cells treated with probe (followed by processing by isoTOP‐ABPP) with a light‐amino‐acid‐labeled standard.
